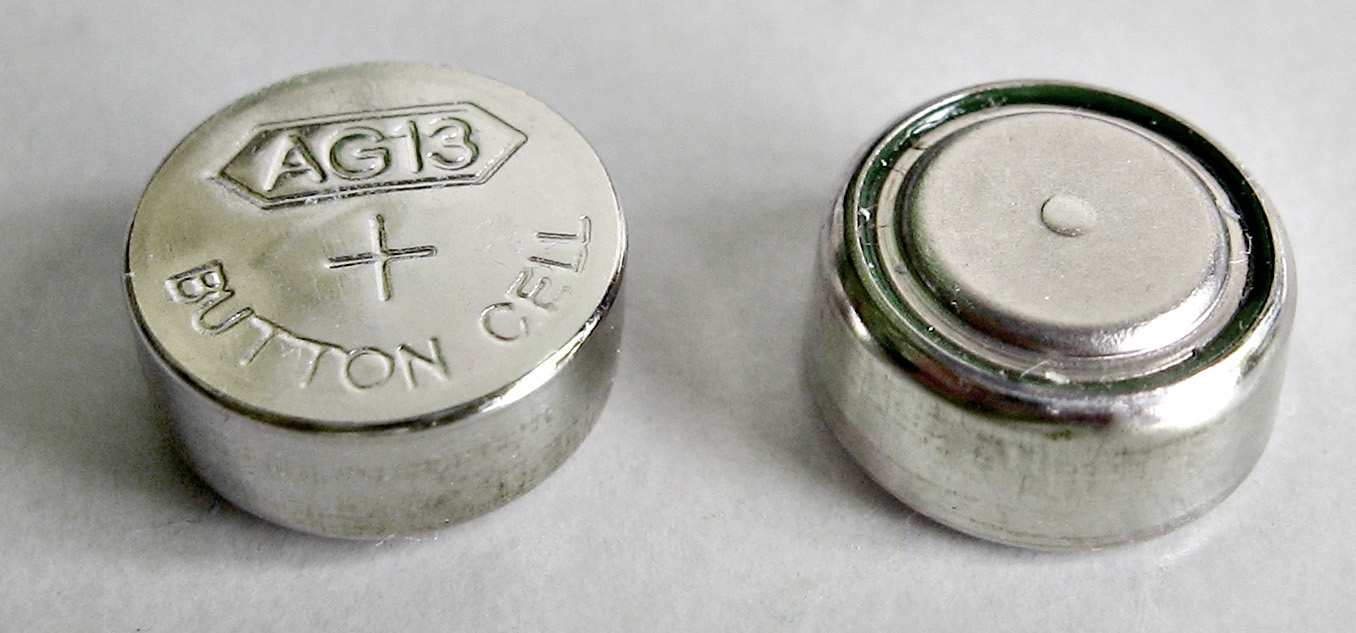
Have you ever wondered what powers your small electronic devices and toys? One of the most common types of batteries found in these gadgets is the AG13 battery. Despite its compact size, the AG13 battery packs quite a punch, providing the necessary energy to keep your devices running smoothly. In this article, we will delve into the world of AG13 batteries, exploring what they are, how they work, and where they are commonly used. Whether you’re curious about the battery in your favorite toy or looking to understand the power source of your electronic device, this article will shed light on the AG13 battery and its importance in the realm of mobile accessories.
Inside This Article
- Definition
- Structure and components
- Common uses
- Chemical Reaction
- Electrochemical cell
- Voltage and Capacity: Pros and Cons of AG13 Batteries
- Advantages
- Disadvantages: How to properly use and dispose of AG13 batteries
- Handling and storage
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Definition
An AG13 battery, also known as LR44, A76, or 357, is a small-sized alkaline button cell battery commonly used in various electronic devices. It belongs to the LR (alkaline) battery series and has a cylindrical shape with a diameter of 11.6mm and a height of 5.4mm. AG13 batteries are known for their compact size and high energy density, making them ideal for powering small electronic devices.
These batteries derive their name from the AG Themed: A for alkaline and G for the mercury content that was used in earlier versions. The replacement LR44 designation refers to the battery’s size and chemistry. The A76 and 357 designations are interchangeable with AG13, indicating their compatibility and similar specifications.
AG13 batteries are commonly found in devices such as calculators, watches, digital thermometers, toys, small electronic gadgets, and medical devices. They provide a reliable and long-lasting power source for these devices, ensuring consistent performance.
Structure and components
The AG13 battery, also known as LR44 or A76, is a small cylindrical battery commonly used in various electronic devices. Despite its compact size, it packs a powerful punch when it comes to providing a reliable source of energy. Let’s take a closer look at its structure and components.
The AG13 battery consists of several key components that work together to generate the electrical power it delivers. The outer shell of the battery is typically made of stainless steel or nickel-plated brass, ensuring durability and protection for the internal components.
1. Anode: The anode is the positive terminal of the battery. It is usually made of zinc, which acts as the primary reactant during the electrochemical process. The anode also contains a gel or electrolyte that facilitates the flow of ions.
2. Cathode: The cathode is the negative terminal of the battery. It is typically made of manganese dioxide (MnO2) mixed with carbon powder, which serves as a conductor. The cathode also contains a separator that prevents direct contact between the anode and cathode, ensuring efficient operation.
3. Electrolyte: The electrolyte is a gel-like substance that acts as a medium for ion flow between the anode and cathode. It generally consists of potassium hydroxide (KOH) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH) mixed with water and other additives. The electrolyte plays a crucial role in facilitating the chemical reactions within the battery.
4. Seal: The seal is a rubber gasket placed at the top of the battery to prevent leakage and also acts as an insulator. It ensures that the electrolyte remains contained within the battery and maintains the integrity of the internal components.
Overall, the structure and components of the AG13 battery work in tandem to produce a steady flow of electrical energy. Whether you’re using it in small electronic devices like calculators, watches, or toys, understanding its structure and how it functions can help you make the most of its power.
Common uses
The AG13 battery, also known as LR44, A76, or 357, is a widely used button cell battery. Its compact size and reliable power make it suitable for a variety of electronic devices. Here are some common uses of AG13 batteries:
- Calculators: AG13 batteries are frequently used in calculators due to their long-lasting power and stable voltage output. Whether it’s a basic pocket calculator or a scientific calculator, chances are it relies on an AG13 battery to keep it running.
- Watches: Many watches, particularly digital watches, rely on AG13 batteries. These batteries provide a consistent and reliable power source, ensuring accurate timekeeping for extended periods.
- Toys: AG13 batteries are commonly found in a wide range of toys, such as electronic toys, remote-controlled cars, and interactive games. Their small size and high energy capacity make them ideal for powering these devices.
- Medical devices: AG13 batteries are frequently used in small medical devices like blood glucose meters, thermometers, and hearing aids. These batteries provide the necessary power to ensure accurate readings and reliable functionality.
- Keyless entry systems: Many key fobs and remote control systems for cars and home security systems rely on AG13 batteries. These batteries supply the power needed for the wireless transmission of signals, making them essential for convenient and secure access.
These are just a few examples of the common uses of AG13 batteries. Their versatility and reliability make them a popular choice for various applications in everyday life.
Chemical Reaction
The chemical reaction that occurs within an AG13 battery is essential for its operation. AG13 batteries, also known as LR44 or A76 batteries, use a chemical reaction to generate electrical energy. This reaction takes place between the battery’s electrolyte solution and its anode and cathode.
The anode of an AG13 battery is typically made of zinc, while the cathode is composed of manganese dioxide. When the battery is in use, the zinc anode undergoes oxidation, releasing electrons in the process. These electrons then flow through an external circuit to power the device the battery is connected to.
Simultaneously, the electrolyte solution facilitates the transport of positively charged ions from the cathode to the anode. This movement of ions helps balance the charge within the battery and maintain continuity in the chemical reaction.
As the zinc anode is oxidized, it reacts with the electrolyte to form zinc oxide, while the manganese dioxide cathode undergoes reduction, ultimately forming manganese (IV) oxide. This chemical transformation allows the battery to generate electrical energy.
Overall, the chemical reaction within an AG13 battery is responsible for producing the flow of electrons, which results in the battery’s ability to power electronic devices. It’s this process that allows AG13 batteries to play a vital role in numerous applications, ranging from calculators and watches to other small electronic devices.
Electrochemical cell
An electrochemical cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy through the process of redox reactions. It consists of two electrodes – an anode and a cathode – immersed in an electrolyte solution. These electrodes are made of different materials, typically metal or metal compounds, that can undergo oxidation and reduction reactions.
When the cell is connected to an external circuit, a chemical reaction occurs at the anode, where electrons are released and flow towards the cathode through the circuit. At the cathode, another chemical reaction takes place, where electrons combine with ions from the electrolyte, completing the circuit and resulting in the generation of electrical energy.
Electrochemical cells can be classified into two types: galvanic cells (also known as voltaic cells) and electrolytic cells. In a galvanic cell, the redox reaction occurs spontaneously, and electrical energy is released. Examples of galvanic cells include batteries. On the other hand, electrolytic cells require an external power source to drive the non-spontaneous reaction, allowing for the electrolysis of substances.
The performance of an electrochemical cell is determined by various factors, including the nature of the electrode materials, the concentration of ions in the electrolyte, and the temperature. These factors influence the voltage and capacity of the cell, impacting its overall efficiency and longevity.
Electrochemical cells are widely used in various applications, including batteries, fuel cells, and electroplating. They provide a reliable and portable source of electrical energy, making them essential in powering devices such as cell phones, laptops, and electric vehicles. Additionally, electrochemical cells play a crucial role in renewable energy systems, such as solar panels and wind turbines, by storing the generated energy for later use.
Voltage and Capacity: Pros and Cons of AG13 Batteries
AG13 batteries, also known as LR44, A76, or 357 batteries, are popular power sources for various devices, including digital watches, calculators, and small electronic toys. Understanding the voltage and capacity of AG13 batteries is essential to know their performance and limitations.
Voltage: AG13 batteries are categorized as alkaline button cell batteries with a nominal voltage of 1.5 volts. This voltage is sufficient to power most low-drain devices effectively. The consistent 1.5-volt output ensures a stable power supply, allowing devices to function optimally without voltage fluctuations.
Capacity: AG13 batteries typically have a capacity range of 110-150 milliampere-hours (mAh). This capacity indicates the amount of energy the battery can hold and how long it can power a device before needing replacement. Higher-capacity AG13 batteries provide longer-lasting power, which is beneficial for applications requiring extended usage.
Pros of AG13 Batteries:
- Wide Availability: AG13 batteries are widely available in various stores and online retailers, making it easy to purchase replacements.
- Compatibility: These batteries are compatible with a range of devices, including watches, calculators, and small electronic gadgets.
- Reliability: AG13 batteries offer a consistent voltage output, ensuring reliable and stable performance for devices.
- Affordability: Compared to other types of batteries, AG13 batteries are relatively affordable, making them a cost-effective choice for powering everyday devices.
Cons of AG13 Batteries:
- Limited Lifespan: AG13 batteries have a finite lifespan and will eventually require replacement, especially for devices with higher power demands.
- Limited Power Output: While AG13 batteries provide sufficient voltage for low-drain devices, they may not be suitable for high-power devices that require a higher voltage output.
- Environmental Impact: Like other disposable batteries, AG13 batteries contribute to electronic waste when not properly disposed of or recycled.
Knowing the voltage and capacity of AG13 batteries allows users to make informed decisions about their usage and potential limitations. While they offer benefits such as wide availability, compatibility, and reliability, it is important to be aware of their limited lifespan, power output, and environmental impact. With proper handling, AG13 batteries can efficiently power a range of devices, providing convenience and functionality.
Advantages
AG13 batteries offer several advantages that make them a popular choice for a variety of applications. Here are some key advantages of using AG13 batteries:
1. Wide Availability: AG13 batteries are widely available and can be easily found in most retail stores, making them convenient to purchase when needed. They are also readily available online, allowing for easy accessibility no matter where you are located.
2. Cost-Effective: AG13 batteries are cost-effective compared to other types of batteries. They are affordable and offer a great balance between price and performance. This makes them an economical choice for both personal and professional use.
3. Long Shelf Life: AG13 batteries have a long shelf life, which means you can store them for extended periods without worrying about them losing their charge. This makes them ideal for emergency kits, backup devices, and other situations where you may need a reliable power source at a moment’s notice.
4. Compact Size: AG13 batteries are compact and lightweight, making them suitable for use in small devices. Their small size allows for easy installation in various electronic devices, including calculators, watches, keychains, and other gadgets.
5. Consistent Performance: AG13 batteries provide a steady and reliable power supply. They deliver a consistent voltage output throughout their lifespan, ensuring that devices powered by AG13 batteries operate smoothly and efficiently.
6. Wide Temperature Range: AG13 batteries are designed to work reliably in a wide temperature range. They can withstand both extreme heat and cold temperatures, making them suitable for use in various environments and climates.
7. Versatile Compatibility: AG13 batteries are compatible with a wide range of electronic devices. They can be used in watches, calculators, remote controls, medical devices, toys, and many other gadgets that require a compact and reliable power source.
Disadvantages: How to properly use and dispose of AG13 batteries
While AG13 batteries offer numerous benefits, it is important to be aware of their disadvantages as well. Here are some drawbacks to consider before using AG13 batteries:
- Limited lifespan: AG13 batteries have a relatively short lifespan compared to other battery types. Their capacity for holding a charge diminishes over time, which means they may need to be replaced more frequently.
- Non-rechargeable: Unlike rechargeable batteries, AG13 batteries are not designed to be recharged. Once they reach the end of their lifespan, they should be properly disposed of and replaced with new batteries.
- Environmental impact: Improper disposal of AG13 batteries can harm the environment. These batteries contain hazardous materials such as mercury, which can contaminate soil and water if not handled and disposed of correctly.
- Higher cost over time: Due to their non-rechargeable nature, continuously replacing AG13 batteries can be more costly in the long run compared to using rechargeable batteries. If your device has higher power demands, this cost can add up quickly.
- Limited compatibility: AG13 batteries have specific dimensions and voltage requirements, which may not be compatible with all devices. Before purchasing AG13 batteries, ensure they are compatible with your device to avoid any issues or damage.
- Disposal challenges: Proper disposal of AG13 batteries requires extra effort. It is important to find a recycling center or collection point that accepts and handles hazardous batteries to ensure they are disposed of safely and responsibly.
To mitigate the disadvantages and ensure the proper use and disposal of AG13 batteries, here are some important guidelines to follow:
- Handle with care: When handling AG13 batteries, avoid damaging the outer cover. Damaged batteries can leak hazardous materials, causing harm to both humans and the environment.
- Store properly: Keep AG13 batteries in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. This will help preserve their lifespan and prevent any potential leaks or damage.
- Dispose responsibly: Do not throw AG13 batteries in the regular trash. Instead, find a local recycling center or collection point that accepts batteries and follows the proper disposal procedures for hazardous materials.
By following these guidelines, you can minimize the disadvantages of AG13 batteries while using them safely and responsibly. Remember, it is always important to prioritize the well-being of the environment and follow proper disposal practices.
Handling and storage
Proper handling and storage of AG13 batteries is essential to ensure their longevity and safety. Here are some important guidelines to follow:
1. Keep AG13 batteries in their original packaging or in a dedicated battery case. This helps protect them from exposure to moisture, dust, and other contaminants.
2. Store AG13 batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Heat can cause the batteries to discharge faster, while cold temperatures can affect their performance.
3. Avoid storing AG13 batteries in locations with high humidity. Moisture can lead to battery corrosion and reduce their overall lifespan.
4. Always keep AG13 batteries away from children and pets. These batteries are small and can pose a choking hazard if swallowed. If ingestion occurs, seek immediate medical attention.
5. Never mix AG13 batteries with other battery types or different brands. Different batteries have different voltage levels and mixing them can cause leakage or damage to devices.
6. When inserting AG13 batteries into devices, make sure to align the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals correctly. Reverse polarity can cause damage to the battery and the device.
7. If a device is not going to be used for an extended period, such as in storage or during travel, it is advisable to remove the batteries to prevent potential leakage and damage.
8. If you notice any abnormalities such as swelling, leakage, or a strange odor coming from the battery, do not use it. Safely dispose of the battery following the recommended recycling and disposal methods.
Remember to always exercise caution and follow the manufacturer’s recommendations when handling and storing AG13 batteries. By doing so, you can ensure their optimal performance and minimize the risk of accidents or damage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the AG13 battery is a small but mighty power source that is widely used in various devices, especially those in the mobile accessories industry. Its compact size and reliable performance make it an ideal choice for gadgets like calculators, watches, key fobs, and many other electronic devices. Whether you need to replace a worn-out battery or stock up on spares, the AG13 battery is a convenient and accessible option.
Remember to always check the specific requirements of your device to ensure compatibility and optimal performance. By taking proper care of your AG13 batteries, such as storing them in a cool, dry place and avoiding exposure to extreme temperatures, you can prolong their lifespan and get the most out of their power.
So, the next time you’re in need of a reliable power source for your mobile accessories, consider the AG13 battery. Its affordability, versatility, and long-lasting performance make it a popular choice among users worldwide.
FAQs
1. What is an AG13 battery?
An AG13 battery, also known as LR44, A76, or 357, is a small button cell battery commonly used in various electronic devices such as digital thermometers, calculators, watches, toys, and remote controls. It is a 1.5-volt alkaline battery that provides reliable power for a wide range of applications.
2. How long does an AG13 battery last?
The lifespan of an AG13 battery can vary depending on the specific device and its usage. Generally, an AG13 battery can last anywhere from 1 to 2 years when used in low-drain devices like watches or calculators. However, in high-drain devices such as electronic toys, the battery may only last a few months. It is important to keep spare AG13 batteries on hand to ensure uninterrupted operation of your electronic devices.
3. Can I replace an AG13 battery with a different type?
While it is highly recommended to use the specific type of battery recommended by the device manufacturer, in some cases, alternative batteries may be compatible. However, it is crucial to ensure that the alternative battery has the same voltage (1.5 volts) and dimensions as the AG13 battery. Using a different type of battery with incompatible specifications may lead to malfunctioning or damage to the device.
4. Where can I buy AG13 batteries?
AG13 batteries are widely available and can be purchased from various sources. They can be found in most electronic stores, department stores, and even online marketplaces. When buying AG13 batteries, it is important to ensure that you are purchasing from a reputable seller to guarantee the quality and authenticity of the batteries.
5. How should I dispose of used AG13 batteries?
AG13 batteries, like other alkaline batteries, should be disposed of properly to prevent environmental contamination. Many communities have designated recycling centers or drop-off locations for used batteries. It is important to follow the guidelines provided by your local waste management authority for the safe and responsible disposal of AG13 batteries. Avoid throwing them in regular trash bins or incinerating them.
