The advancement of medical technology has brought about innovative treatments for various conditions, including cancer. One such treatment is blue light therapy, which has gained popularity in recent years as a non-invasive option for fighting cancer cells. But what exactly is blue light treatment for cancer, and how does it work? In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of this treatment method, exploring its benefits, applications, and potential side effects. Whether you are a cancer patient or simply curious about the latest advancements in cancer treatment, this article aims to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of blue light therapy’s role in combating cancer. So let’s shed some light on the subject and explore the world of blue light treatment for cancer.
Inside This Article
- Blue Light Treatment: An Overview
- How Does Blue Light Treatment Work?
- Types of Cancer Treated with Blue Light Therapy
- Benefits and Risks of Blue Light Treatment for Cancer
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Blue Light Treatment: An Overview
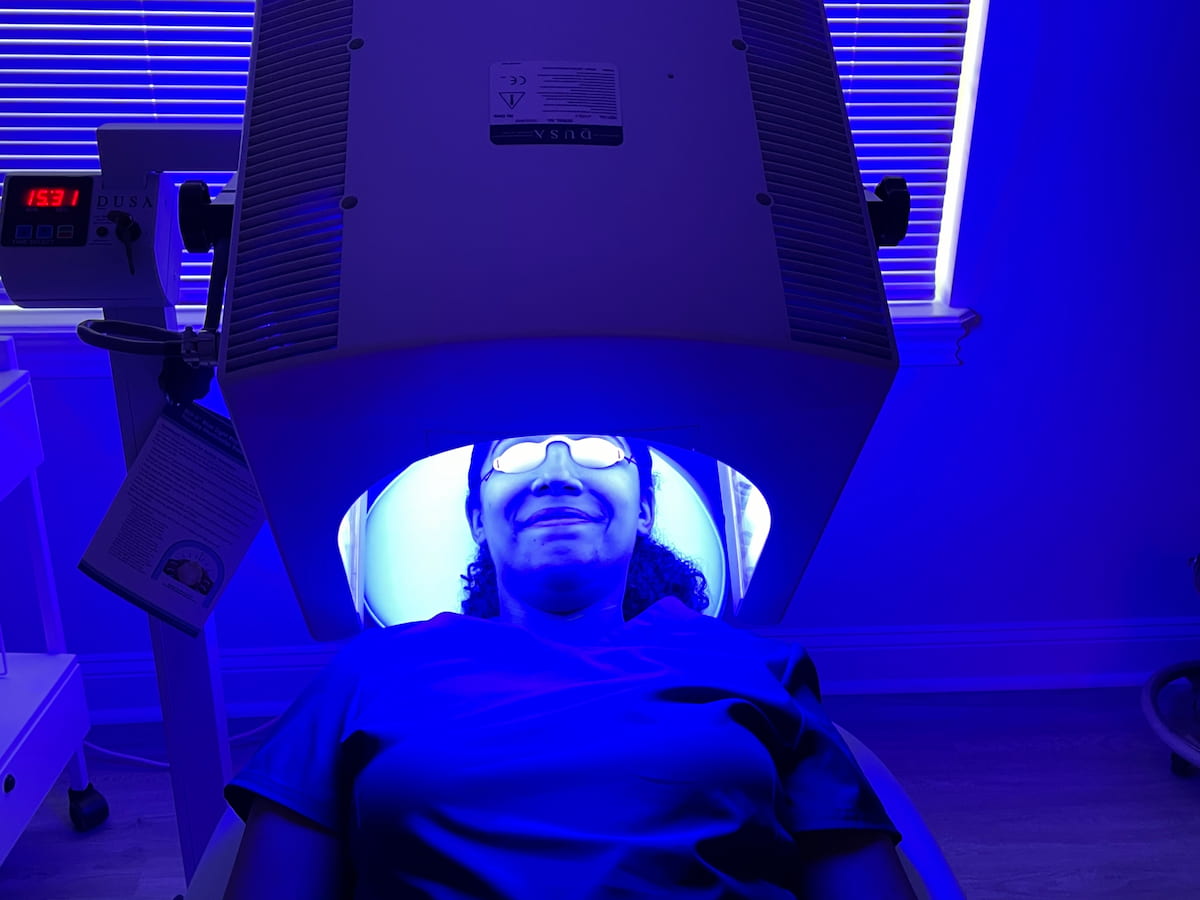
Blue light treatment, also known as photodynamic therapy, is a cutting-edge treatment option for various types of cancer. It involves using a specific wavelength of light to activate light-sensitive drugs, known as photosensitizers, which are selectively absorbed by cancer cells. This innovative treatment approach has gained traction in recent years due to its targeted and minimally invasive nature.
The concept behind blue light treatment is to selectively destroy cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy surrounding tissue. The process begins with the administration of a photosensitizer, typically through injection or topical application. The photosensitizer is then allowed to accumulate in cancer cells over a certain period of time.
Once the photosensitizer has accumulated, blue light of a specific wavelength is directed onto the target area. The photosensitizer absorbs the light and produces a reactive oxygen species, which induces a chain of reactions leading to the destruction of cancer cells. This process is highly precise, allowing for targeted treatment and reduced side effects compared to traditional cancer therapies.
Blue light treatment can be used to treat various types of cancer, including skin cancer, esophageal cancer, lung cancer, and certain types of head and neck cancers. It is often employed as an alternative or adjunct therapy to surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy. The specific application and effectiveness of blue light treatment will depend on the individual case, stage of cancer, and overall treatment plan.
One of the key advantages of blue light treatment is its potential to selectively target cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. This targeted approach minimizes damage to surrounding organs and tissues and reduces the risk of side effects commonly associated with conventional cancer treatments. Additionally, blue light treatment can be repeated if necessary, allowing for ongoing cancer management.
However, as with any medical procedure, there are risks and potential side effects associated with blue light treatment. Common side effects may include skin redness, swelling, and temporary sensitivity to light. In some cases, more serious side effects, such as blistering or changes in skin pigmentation, may occur. It is important to discuss the potential benefits and risks of blue light treatment with your healthcare provider to determine if it is an appropriate treatment option for your specific cancer diagnosis.
How Does Blue Light Treatment Work?
Blue light treatment, also known as photodynamic therapy (PDT), is a revolutionary medical approach used to treat various types of cancer. This innovative treatment utilizes a combination of a photosensitizing drug and blue light to target and destroy cancer cells.
The process begins by administering the photosensitizing drug, which is typically given intravenously or applied topically to the affected area. This drug, which is harmless in its inactive state, selectively accumulates in cancerous cells, making them more susceptible to the effects of the blue light.
Once the photosensitizing drug has had sufficient time to localize in the cancer cells, the blue light is applied to the area. The blue light activates the drug, causing it to release oxygen molecules that create a chemical reaction within the cancer cells. This reaction damages or destroys the cancer cells, inhibiting their ability to grow and spread.
The effectiveness of blue light treatment relies on the specificity of the photosensitizing drug to target cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissue. This targeted approach minimizes side effects and maximizes the therapeutic effect of the treatment.
The blue light used in this therapy is typically delivered through specialized devices. These devices emit specific wavelengths of light that are optimal for activating the photosensitizing drug. The duration and intensity of the blue light exposure depend on the type and location of the cancer being treated.
It’s important to note that blue light treatment is a non-invasive procedure, and no surgical intervention is required. This makes it an attractive option for patients who are seeking alternatives to surgery or who may not be suitable candidates for other treatments.
Overall, blue light treatment offers a promising approach to cancer treatment, providing a targeted and minimally invasive way to destroy cancer cells. It offers several advantages, including reduced side effects, preservation of healthy tissue, and the potential to treat a wide range of cancers.
Types of Cancer Treated with Blue Light Therapy
Blue light therapy is a non-invasive treatment option that has shown promise in treating various types of cancer. While it is not a standalone cure, it can be used as an adjuvant therapy alongside other conventional treatments like surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Here are some common types of cancer that can be treated with blue light therapy:
1. Skin Cancer: Blue light therapy is particularly effective in treating certain types of skin cancer, such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. It works by targeting and destroying cancer cells on the surface of the skin without harming the surrounding healthy tissue.
2. Actinic Keratosis: Actinic keratosis refers to pre-cancerous skin lesions caused by long-term sun exposure. Blue light therapy can be used to selectively target and eliminate these abnormal cells, reducing the chances of them developing into full-blown skin cancer.
3. Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer: Apart from basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, blue light therapy can also be effective in treating other types of non-melanoma skin cancer, including cancer of the sweat glands and hair follicles.
4. Bladder Cancer: Blue light therapy has shown promising results in the treatment of early-stage bladder cancer. It involves the use of a photosensitizing agent that is selectively absorbed by cancer cells in the bladder. When exposed to blue light, the agent produces toxic free radicals that destroy the cancer cells.
5. Lung Cancer: While blue light therapy is not commonly used as a primary treatment for lung cancer, it can be employed in certain cases. It can be used in combination with other treatments to target specific tumors or areas of the lungs.
6. Prostate Cancer: Blue light therapy is being investigated as a potential treatment for prostate cancer. It involves the use of a light-sensitive drug that is injected into the bloodstream and then activated by blue light to destroy cancer cells in the prostate gland.
It’s important to note that the use of blue light therapy for cancer treatment should always be discussed with a healthcare professional. They will assess the individual’s specific condition and determine whether blue light therapy is a suitable option. While it can be effective in certain cases, its efficacy and potential side effects may vary depending on the type and stage of cancer being treated.
Benefits and Risks of Blue Light Treatment for Cancer
When it comes to treating cancer, blue light therapy has gained significant attention in recent years. This innovative treatment approach utilizes a non-invasive method to target cancer cells and offers several benefits. However, like any medical procedure, blue light treatment also carries its fair share of risks. In this section, we will explore the potential benefits and risks of blue light therapy for cancer.
Benefits:
- Non-invasive: One of the major advantages of blue light treatment is that it is a non-invasive procedure. Unlike surgeries or radiation therapy, blue light therapy does not require incisions or the use of external radiation sources.
- Precision: Blue light therapy specifically targets cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy surrounding tissues. This targeted approach helps to reduce the risk of complications and side effects.
- Pain-free: Blue light therapy is generally painless and does not require anesthesia. Patients can undergo the treatment without experiencing significant discomfort.
- Quick procedure: The duration of blue light treatment sessions can vary depending on the type and stage of cancer. However, in many cases, the procedure is relatively short, allowing patients to resume their daily activities soon after treatment.
- Limited side effects: Compared to other cancer treatment methods, blue light therapy tends to have fewer side effects. Common side effects may include mild redness or swelling in the treated area, which usually subsides within a few days.
Risks:
- Photosensitivity: One of the main risks associated with blue light treatment is photosensitivity. Exposing the skin to blue light can make it more sensitive to sunlight, potentially leading to sunburn or other skin reactions. It is crucial for patients to protect treated areas from direct sunlight for a certain period after each session.
- Unknown long-term effects: As blue light therapy is a relatively new treatment approach, there is limited long-term data regarding its potential risks. More research is needed to fully understand the possible long-term effects of repeated blue light exposure on the body.
- Effectiveness limitations: While blue light therapy shows promise in treating certain types of cancer, it may not be effective for all forms. The success of the treatment often depends on the stage and location of the cancer. Consulting with an oncologist or medical professional is key in determining whether blue light therapy is a suitable option for an individual’s specific case.
It is important to note that the benefits and risks of blue light treatment for cancer can vary depending on the patient and the specifics of their condition. It is crucial to consult with a medical professional to discuss individual risk factors, potential benefits, and any additional treatment options available.
Conclusion
Blue light treatment for cancer, also known as photodynamic therapy (PDT), is a promising therapeutic approach that shows great potential in the field of oncology. By utilizing specific wavelengths of light, it can effectively target and destroy cancer cells in a targeted manner.
This non-invasive and minimally invasive treatment option offers several advantages, including fewer side effects and a shorter recovery time compared to more traditional cancer treatments. Additionally, it can be used in combination with other treatments, such as surgery or chemotherapy, to enhance their effectiveness.
While blue light treatment for cancer is still being researched and refined, it represents a significant advancement in cancer therapy. As technology continues to progress, it’s likely that we will see further developments and refinements in this field, ultimately leading to improved outcomes for cancer patients.
FAQs
1. What is blue light treatment for cancer?
Blue light treatment for cancer, also known as photodynamic therapy (PDT), is a non-invasive treatment that uses a combination of a light-sensitive drug and a specific wavelength of light to target and destroy cancer cells. The light activates the drug, which then produces toxic oxygen molecules that kill the cancer cells.
2. How does blue light treatment work?
During blue light treatment, the patient receives a photosensitizing drug either by injection or topically. The drug is absorbed by both cancerous and normal cells. When the drug is activated by the blue light, it produces a form of oxygen that is toxic to the cancer cells, damaging their DNA and causing cell death.
3. What types of cancer can be treated with blue light treatment?
Blue light treatment has been used to treat various types of cancer, including skin cancer, lung cancer, esophageal cancer, and certain types of head and neck cancers. It is also effective in treating precancerous conditions such as actinic keratosis.
4. Are there any side effects or risks associated with blue light treatment?
Like any medical procedure, blue light treatment carries some potential side effects and risks. Common side effects include swelling, redness, and temporary sensitivity to light. In rare cases, more severe side effects such as blistering, scarring, or changes in skin pigmentation may occur. It is essential to consult with a medical professional to assess the potential risks and benefits for your specific condition.
5. How long does a blue light treatment session typically last?
The duration of a blue light treatment session can vary depending on the type and stage of cancer being treated. Generally, a session lasts for about 30 minutes to a few hours. The specific treatment protocol will be determined by the healthcare professional based on individual factors and the specific type of cancer being targeted.
