Handling unstructured data can be a daunting task, but it is becoming increasingly important in today’s digital age. With the vast amount of information generated through emails, social media, documents, and other sources, businesses need effective strategies to make sense of this data and derive valuable insights. Unstructured data refers to information that doesn’t fit neatly into traditional databases, such as text, images, audio files, and videos. Organizations that can harness the power of unstructured data gain a competitive edge by understanding customer sentiment, detecting patterns and trends, and making informed decisions. In this article, we will explore various techniques and tools that can help businesses effectively handle unstructured data and unlock its full potential.
Inside This Article
- What is Unstructured Data?
- Challenges of Handling Unstructured Data
- Strategies for Handling Unstructured Data
- Tools and Technologies for Handling Unstructured Data
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Unstructured Data?
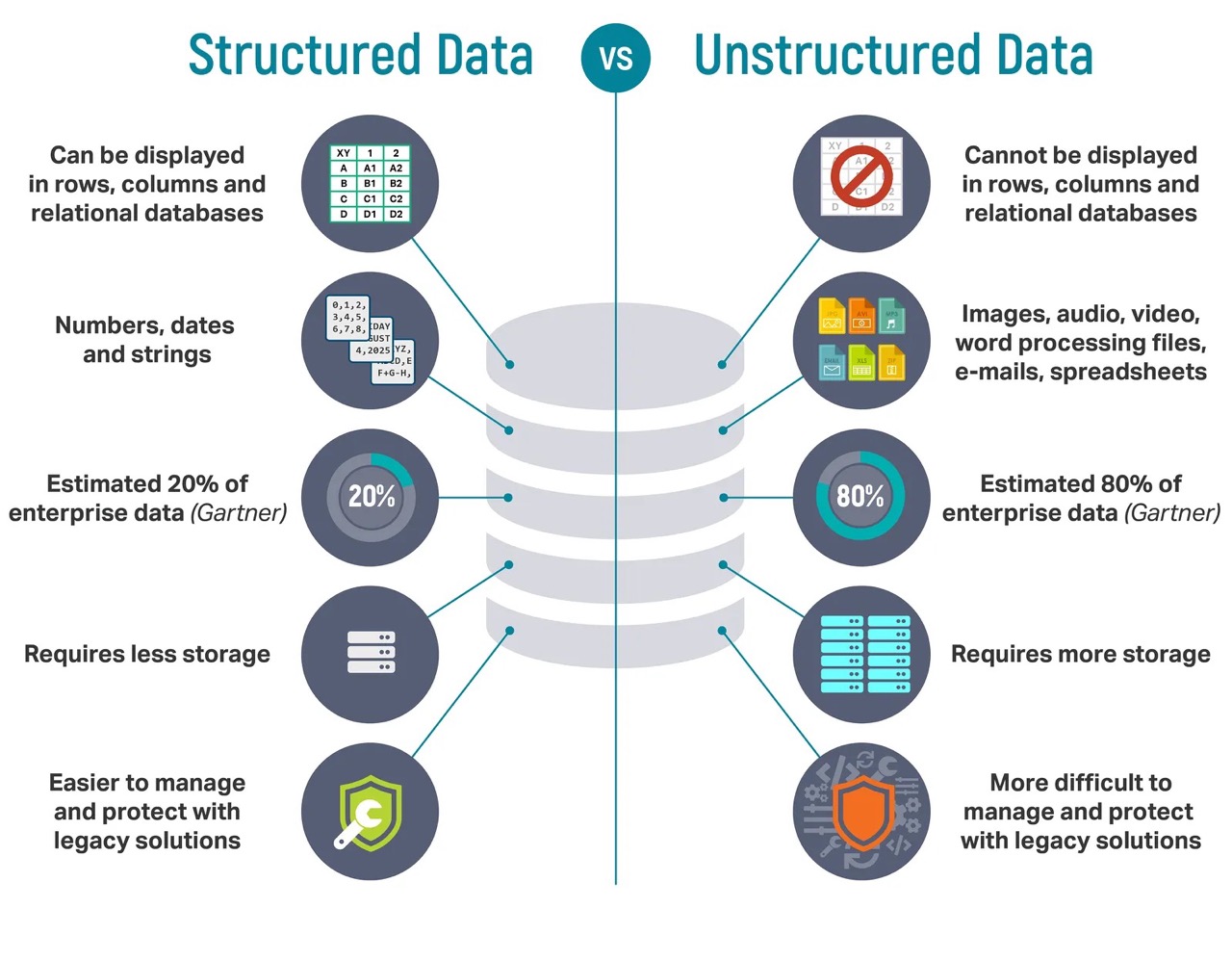
Unstructured data refers to any digital information that does not have a predefined format or organized structure. Unlike structured data, which is organized into tables and databases, unstructured data does not fit neatly into rows and columns. Instead, it is often in the form of text documents, emails, images, videos, social media posts, audio files, and more.
This type of data is challenging to analyze and process using traditional relational database management systems. It lacks a consistent and uniform structure, making it difficult to store, search, and retrieve information effectively. Unstructured data accounts for a significant portion of the data generated by individuals and organizations, and its volume is continuously growing with the proliferation of digital technologies.
Examples of unstructured data include customer reviews, social media conversations, sensor data, surveillance footage, research papers, blog posts, and multimedia content like podcasts and webinars. This data often contains valuable insights and hidden patterns that organizations can leverage to gain a competitive edge or make informed business decisions.
So, the challenge lies in finding ways to handle and make sense of this vast amount of unstructured data. Businesses need effective strategies, tools, and technologies to extract valuable information, discover patterns, and derive meaningful insights from unstructured data sets.
Challenges of Handling Unstructured Data
Unstructured data refers to information that does not follow a predefined or organized format, such as text documents, emails, social media posts, images, audio files, and videos. While unstructured data holds valuable insights, it presents several challenges that businesses need to overcome to harness its full potential. Let’s explore some of the major challenges of handling unstructured data.
1. Lack of organization: Unstructured data is typically not organized in a structured manner, making it difficult to search, categorize, and analyze. With no predefined schema or format, businesses must invest significant time and resources to process and extract meaningful information from unstructured data.
2. Volume and variety: Unstructured data is produced in massive volumes and comes in various formats. This poses a challenge in terms of storage and processing power required to handle the data efficiently. Businesses need robust infrastructure and storage systems to manage the sheer volume and variety of unstructured data.
3. Data integrity and quality: Unstructured data is often prone to errors, inconsistencies, and duplication. Without proper data cleansing and normalization, the accuracy and reliability of the insights derived from unstructured data may be compromised. Businesses must invest in data cleansing and quality control processes to ensure the integrity of the data.
4. Context and semantics: Understanding the context and semantics of unstructured data is crucial for accurate analysis. However, unstructured data often lacks contextual information, making it challenging to interpret and derive insights. Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine learning techniques can help in extracting meaning and understanding the context of unstructured data.
5. Privacy and security: Unstructured data may contain sensitive and confidential information, making privacy and security a significant concern. Businesses must implement robust security measures and data access controls to protect unstructured data from unauthorized access, breaches, and potential legal implications.
6. Data integration: Integrating unstructured data with structured data sources is essential to gain a holistic view of the information. However, integrating unstructured data with structured databases can be complex, requiring data transformation and normalization. Businesses need to establish effective data integration processes to leverage the full potential of unstructured data.
Overcoming these challenges requires a combination of advanced technologies, data management strategies, and expertise in handling unstructured data. By addressing these challenges, businesses can unlock valuable insights, make data-driven decisions, and gain a competitive advantage in today’s data-driven world.
Strategies for Handling Unstructured Data
Dealing with unstructured data can be a complex task, but with the right strategies, you can effectively tame the data chaos. Here are some key strategies to help you handle unstructured data:
1. Data Classification: The first step towards managing unstructured data is to classify it into relevant categories. This can be done by leveraging natural language processing algorithms and machine learning techniques. Classifying the data based on its content, context, or purpose allows for easier organization and retrieval.
2. Text Analysis: Analyzing the textual content within unstructured data can provide valuable insights. Techniques such as sentiment analysis, keyword extraction, and entity recognition can help extract meaningful information from unstructured text. This analysis can aid in understanding customer sentiments, identifying trends, and making data-driven decisions.
3. Metadata Extraction: Extracting metadata from unstructured data helps in organizing and retrieving information efficiently. Metadata refers to the descriptive information about the data, such as timestamps, authors, file types, and tags. Capturing and utilizing metadata enables better searchability, content organization, and data governance.
4. Data Integration: Integrating unstructured data with structured data sources can provide a holistic view of your organization’s data landscape. By combining data from various sources, such as databases, files, social media, and emails, you can gain deeper insights and identify new patterns and relationships.
5. Data Cleansing: Unstructured data often comes with inconsistencies, errors, and duplicates. Data cleansing involves identifying and correcting these issues to ensure data quality and reliability. Automated data cleansing tools and techniques can help streamline this process and improve the accuracy and usability of your data.
6. Data Storage and Management: Choosing the right data storage and management solution is crucial for handling unstructured data effectively. This includes considering factors such as scalability, security, accessibility, and the ability to handle different types of unstructured data. Cloud storage solutions, data lakes, or specialized unstructured data management systems can simplify data storage and retrieval.
7. Data Governance and Compliance: Establishing governance policies and ensuring compliance with data regulations is essential when dealing with unstructured data. This involves defining data ownership, access controls, data retention policies, and ensuring data privacy and security. Implementing robust data governance practices helps maintain data integrity and reduce risks associated with unstructured data.
8. Continuous Monitoring and Analysis: Unstructured data is constantly evolving. It’s important to establish processes for continuous monitoring and analysis to stay on top of any changes or new data. This can involve setting up automated data pipelines, real-time monitoring tools, and implementing data analytics frameworks to extract insights from the evolving unstructured data.
By adopting these strategies, organizations can effectively handle and leverage the full potential of unstructured data. Efficient management of unstructured data can lead to valuable business insights, improved decision-making, and enhanced customer experiences.
Tools and Technologies for Handling Unstructured Data
When it comes to handling unstructured data, there are a variety of tools and technologies available that can streamline the process. These tools leverage advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to extract meaningful insights from unstructured data sources such as text documents, images, videos, and social media feeds. Let’s explore some of the key tools and technologies that can help businesses effectively handle unstructured data:
1. Natural Language Processing (NLP) Libraries: NLP libraries, such as NLTK (Natural Language Toolkit) and SpaCy, provide a wide range of functionalities for processing and analyzing text data. These libraries offer capabilities like text tokenization, named entity recognition, sentiment analysis, and part-of-speech tagging, enabling businesses to extract valuable information from unstructured text documents.
2. Text Analytics Platforms: Text analytics platforms, like IBM Watson and Google Cloud Natural Language Processing, offer comprehensive solutions for extracting insights from unstructured text data. These platforms use machine learning models to analyze text documents, identify key topics, sentiments, and entities, and provide advanced data visualization capabilities for easy interpretation.
3. Optical Character Recognition (OCR) Tools: OCR tools, such as ABBYY FineReader and Tesseract, convert scanned documents and images into editable text formats. These tools use image processing techniques and machine learning algorithms to recognize characters and extract text, making it easier to analyze and extract information from unstructured data in the form of images or physical documents.
4. Image and Video Analysis Platforms: Image and video analysis platforms, like Amazon Rekognition and Microsoft Azure Computer Vision, utilize deep learning models to analyze and interpret visual content. These platforms can recognize objects, faces, and scenes in images and videos, enabling businesses to gain valuable insights from unstructured visual data.
5. Social Media Analytics Tools: Social media analytics tools, such as Hootsuite and Brandwatch, allow businesses to collect, analyze, and derive insights from unstructured data generated on various social media channels. These tools offer sentiment analysis, trend identification, and social listening capabilities, enabling businesses to understand customer preferences, engage in social media marketing, and make data-driven decisions.
6. Data Integration and Preparation Tools: Data integration and preparation tools, like Apache Nifi and Talend, simplify the process of gathering and transforming unstructured data from multiple sources. These tools provide functionalities for data cleansing, data transformation, and data enrichment, ensuring that the unstructured data is properly formatted and ready for analysis.
7. Big Data Analytics Platforms: Big data analytics platforms, such as Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark, offer scalable and distributed processing capabilities for analyzing large volumes of unstructured data. These platforms allow businesses to leverage parallel processing and distributed computing techniques to extract insights from massive amounts of unstructured data in real-time.
8. Knowledge Graphs: Knowledge graphs, like Neo4j and Stardog, provide a powerful way to represent and connect unstructured data through semantic relationships. These graphs enable businesses to organize and query unstructured data effectively, making it easier to discover hidden connections, extract meaningful insights, and drive informed decision-making.
By leveraging these tools and technologies, businesses can effectively handle and derive valuable insights from unstructured data, unlocking its true potential for driving growth and innovation.
Overall, successfully handling unstructured data is essential for businesses looking to harness the power of information in today’s digital age. With the exponential growth of data, organizations must adapt and employ effective techniques for managing, analyzing, and extracting value from unstructured data.
By implementing the right tools, technologies, and approaches, companies can unlock valuable insights, make data-driven decisions, enhance customer experiences, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
Remember that unstructured data is a valuable resource waiting to be tapped into. Whether it’s text, images, audio, or video, extracting meaningful information from this wealth of unstructured data can lead to significant business opportunities and growth.
So, take the time to understand your unstructured data sources, choose the right data management and analytics solutions, and explore the various techniques available to transform unstructured data into actionable insights. By doing so, you’ll position your business for success in the data-driven world of tomorrow.
FAQs
-
What is unstructured data?
Unstructured data refers to any data that does not conform to a predefined data model or organization. It lacks a specific format and does not fit neatly into traditional rows and columns like structured data. -
Why is unstructured data challenging to handle?
Unstructured data presents challenges because it is typically large in volume, difficult to analyze, and contains a wide variety of formats including text files, images, videos, social media posts, and more. Unlike structured data, it doesn’t have a pre-defined structure or set schema, making it harder to extract meaningful insights. -
What are some common sources of unstructured data?
Unstructured data can come from various sources such as social media platforms, customer feedback, emails, audio recordings, video files, sensor data, and documents like PDFs, Word files, and spreadsheets. These sources generate vast amounts of unstructured data that organizations can utilize to gain valuable insights. -
How can organizations handle unstructured data?
To handle unstructured data effectively, organizations can use technologies like natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and artificial intelligence (AI) to extract valuable information. They can also employ data mining techniques to identify patterns, sentiment analysis to understand customer feedback, and image recognition algorithms to process visual data. -
What are the benefits of analyzing unstructured data?
Analyzing unstructured data can provide organizations with valuable insights, including improving customer experience by understanding sentiment analysis, making data-driven decisions, detecting fraud or security threats, enhancing product development, and optimizing overall operational efficiency. By harnessing the power of unstructured data, organizations can gain a competitive edge in today’s data-driven economy.
