When it comes to diagnosing and troubleshooting issues with your vehicle, the On-Board Diagnostics-II (OBD-II) system plays a crucial role. At the heart of this system is the Data Link Connector (DLC), which is a standardized port typically located under the dashboard. The DLC allows for the connection of various diagnostic tools and devices to retrieve valuable information and codes from the vehicle’s onboard computer system. Among the 16 terminals of the OBD-II DLC, Terminal 16 holds a specific purpose. In this article, we will explore the functionality of Terminal 16 and understand how it contributes to the overall diagnostic process. So, if you’re curious to learn more about the inner workings of your vehicle’s OBD-II system, keep reading to discover the significance of Terminal 16.
Inside This Article
- Purpose of the OBD-II Data Link Connector
- Terminal 16 Functionality
- Common Uses of Terminal 16 of the OBD-II Data Link Connector
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Purpose of the OBD-II Data Link Connector
The OBD-II Data Link Connector (DLC) is a crucial component in modern vehicles that serves multiple purposes. It is essentially a standardized port that allows communication between the vehicle’s onboard computer systems and external devices, such as diagnostic tools and accessories.
The primary purpose of the OBD-II DLC is to provide access to the vehicle’s diagnostic information. It allows technicians and vehicle owners to retrieve valuable data about the vehicle’s performance, emissions, and overall health. This information is essential for identifying and troubleshooting any issues or malfunctions that the vehicle may be experiencing.
The OBD-II DLC also plays a key role in emissions testing and compliance. By connecting emissions testing equipment to the DLC, authorities can evaluate the vehicle’s emissions levels to ensure they meet the regulatory standards set by environmental agencies. This helps in reducing air pollution and promoting a cleaner environment.
Moreover, the DLC is the gateway for accessing various vehicle systems and sensors. It allows for reading real-time parameters like engine speed, coolant temperature, fuel trim, and more. This information is valuable for vehicle tuning, performance upgrades, or diagnosing specific issues related to engine or drivetrain components.
Additionally, the DLC facilitates software updates and reprogramming of the vehicle’s onboard computer systems. Manufacturers can use this port to install new software versions, fix bugs, or enhance the functionality of the vehicle. It also enables access to vehicle-specific data, enabling mechanics to perform software updates or adjust certain settings as required.
The OBD-II DLC has become an essential tool for automotive enthusiasts, technicians, and vehicle owners. Its purpose extends beyond diagnostics and emissions testing to encompass performance tuning, software updates, and customization. It acts as a bridge between the vehicle and external devices, facilitating better control, troubleshooting, and optimization of the vehicle’s systems.
Terminal 16 Functionality
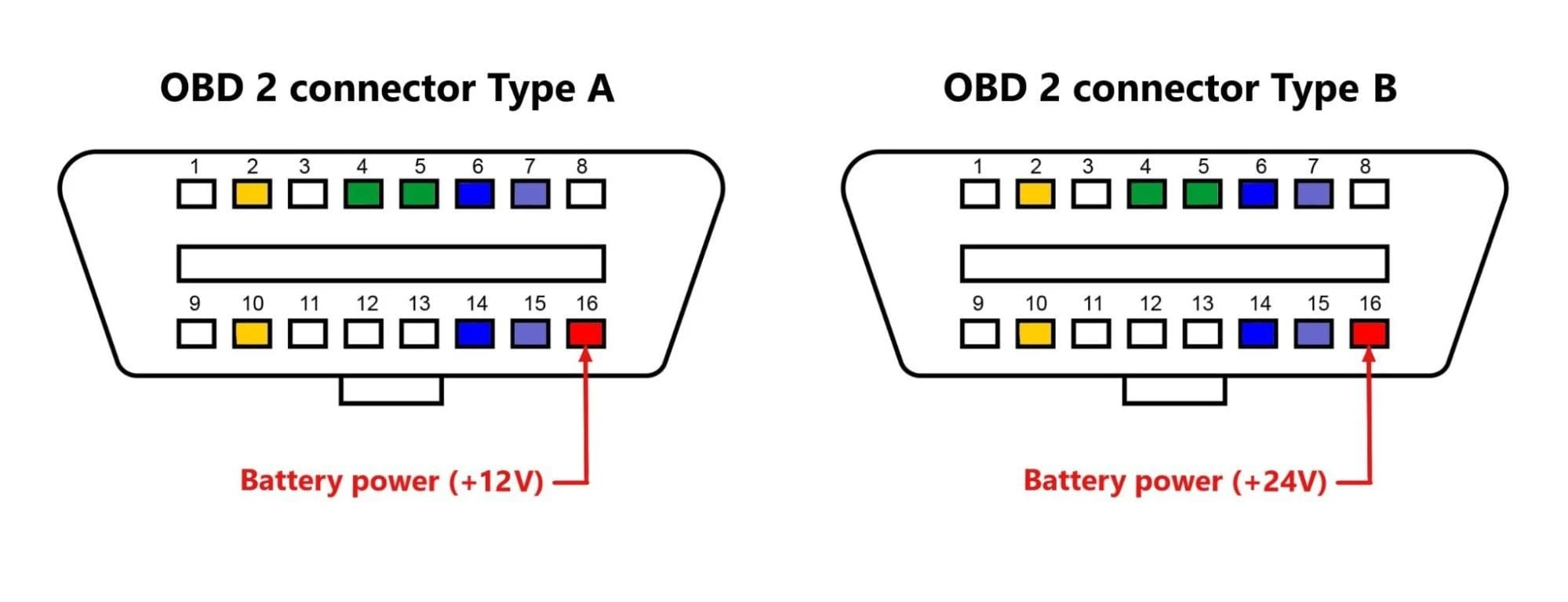
Terminal 16 of the OBD-II Data Link Connector plays a crucial role in the functioning of the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics system. It serves as an interface that allows communication between the vehicle’s electronic control unit (ECU) and external devices. This terminal is typically used for a specific purpose and can provide valuable information and functionality for both vehicle owners and technicians.
One of the primary functions of Terminal 16 is to supply power to external devices connected to the OBD-II port. It provides a 12-volt power supply, also known as the accessory power, which enables the functioning of various mobile accessories and diagnostic tools that are designed to interface with the vehicle’s ECU. This power supply ensures that the connected devices have the necessary power to operate efficiently.
In addition to providing power, Terminal 16 is also responsible for establishing communication between the vehicle and external devices. It serves as a data link between the ECU and diagnostic tools, allowing for the exchange of vital information related to the vehicle’s performance and diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). This data exchange enables technicians to diagnose and troubleshoot various issues, such as engine malfunctions, emission problems, and sensor failures.
Furthermore, Terminal 16 can be used for programming and reprogramming the ECU. It allows technicians to update the vehicle’s software or modify specific parameters to enhance the vehicle’s performance or address any software-related issues. This capability is particularly beneficial for performance tuning, emissions testing, and overall system optimization.
Moreover, Terminal 16 of the OBD-II Data Link Connector can also be utilized for vehicle tracking and monitoring purposes. By connecting a compatible tracking device, such as a GPS tracker, to this terminal, users can keep track of the vehicle’s location, monitor its speed, and even receive real-time notifications in case of unauthorized vehicle movement. This functionality is widely used in fleet management, ensuring enhanced security and efficient tracking of multiple vehicles.
Common Uses of Terminal 16 of the OBD-II Data Link Connector
Terminal 16 of the OBD-II Data Link Connector, also known as the DLC, plays a crucial role in the communication between the vehicle’s onboard computer and external devices. This terminal serves as a gateway for various diagnostic and programming functions, contributing to the overall efficiency and performance of the vehicle.
Here are some common uses of Terminal 16 of the OBD-II Data Link Connector:
- Vehicle Diagnostics: One of the primary uses of Terminal 16 is for vehicle diagnostics. When connected to a diagnostic tool or scanner, it allows technicians to access the vehicle’s diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), view real-time data, and perform advanced diagnostic tests. With this information, mechanics can accurately identify and resolve issues, ensuring optimal performance and reduced repair time.
- Emissions Testing: Another important use of Terminal 16 is in emissions testing. The DLC provides access to emissions-related data from the vehicle’s onboard computer, allowing regulators to measure and analyze the levels of pollutants emitted by the vehicle. This data is crucial for assessing compliance with environmental regulations and developing effective measures to reduce emissions.
- Vehicle Programming: Terminal 16 also facilitates vehicle programming. It enables technicians to update and reflash the vehicle’s software, including engine control modules (ECMs), transmission control modules (TCMs), and other electronic components. This capability is especially valuable when installing software updates, resolving software-related issues, or customizing certain vehicle settings.
- Telematics Integration: Terminal 16 is utilized for integrating telematics systems into the vehicle. Telematics systems collect and transmit data related to vehicle location, performance, and driver behavior. By connecting the telematics device to the DLC, this data can be accessed and utilized for fleet management, remote vehicle monitoring, and various other applications.
- Performance Tuning: Terminal 16 is often used by performance enthusiasts and tuners for ECU (Engine Control Unit) tuning. By connecting to the DLC, they can access the relevant data and parameters necessary to fine-tune the engine’s performance. This includes adjustments to fuel and ignition timing, turbo boost levels, and other engine parameters to optimize power, torque, and overall performance.
- Mobile Accessories: Terminal 16 serves as a crucial connection point for various mobile accessories, such as Bluetooth adapters, GPS trackers, and hands-free calling kits. These accessories can be plugged into the OBD-II DLC, leveraging the terminal’s power and communication capabilities to enhance functionality and compatibility with the vehicle’s onboard systems.
These are just a few examples of the many common uses of Terminal 16 of the OBD-II Data Link Connector. Its versatility and integral role in vehicle diagnostics and communication make it an essential component for both technicians and vehicle owners alike.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Terminal 16 of the OBD-II Data Link Connector is a crucial component in the vehicle’s diagnostic system. It serves as the power source for certain mobile accessories, enabling them to connect to the vehicle’s onboard computer and retrieve valuable data. Whether it’s a Bluetooth OBD-II scanner or a mobile phone charger, Terminal 16 provides the necessary power supply to keep these devices functioning properly. By understanding the purpose of Terminal 16, car owners and technicians can make the most of the OBD-II system and enhance their diagnostic capabilities. So, next time you connect a mobile accessory to your vehicle, remember the significance of Terminal 16 and its role in powering your device.
FAQs
1. What is the purpose of Terminal 16 on the OBD-II Data Link Connector?
Terminal 16 on the OBD-II Data Link Connector is known as the Battery Positive Voltage pin. It is used to provide power to various accessories and devices connected to the OBD-II port. This includes devices like code readers, scan tools, and other diagnostic equipment.
2. Can I use Terminal 16 to power my mobile device?
Yes, you can utilize Terminal 16 to power your mobile devices, but it is important to keep in mind that the power output might be limited. While it can provide power to charge most mobile devices, it may not be sufficient for high-power-consuming devices like tablets or laptops. It is always recommended to use a dedicated charger or power source for such devices.
3. Is it safe to connect accessories directly to Terminal 16?
While it is technically possible to connect accessories directly to Terminal 16, it is generally not recommended. The OBD-II Data Link Connector is primarily designed for diagnostic purposes and connecting devices directly to the terminal may interfere with the proper functioning of the vehicle’s systems. It is advisable to use a dedicated power source or an approved OBD-II adapter for connecting accessories.
4. Are there any risks involved with using Terminal 16?
Using Terminal 16 to power accessories does come with certain risks. Since the OBD-II port is directly connected to the vehicle’s electrical system, there is a possibility of overloading the circuit and causing damage to the vehicle’s electronics. It is crucial to ensure that the connected devices draw power within the specified limits and do not exceed the capacity of the OBD-II port.
5. Can using Terminal 16 affect the vehicle’s battery?
In most cases, using Terminal 16 to power low-power-consuming accessories will not significantly impact the vehicle’s battery life. However, if high-power-drawing devices are connected and left running for extended periods without the engine running, it can drain the battery. It is important to monitor the power usage and avoid leaving accessories connected when the vehicle is not in use for long periods.
