In the ever-evolving world of technology, the need for faster and more efficient data transfer is paramount. One of the key components that enables high-speed data transmission in modern computers is a PCIe connector. But what exactly is a PCIe connector, and how does it contribute to the performance of your device? In this article, we will delve into the world of PCIe connectors, exploring their purpose, functionality, and significance in the realm of computer hardware. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or just curious about the inner workings of your computer, this article will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of PCIe connectors and their role in powering the data transfer capabilities of today’s devices.
Inside This Article
- What Is a PCIe Connector
- Definition of a PCIe Connector
- Types of PCIe Connectors
- Functions of a PCIe Connector
- Common Uses of PCIe Connectors
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What Is a PCIe Connector
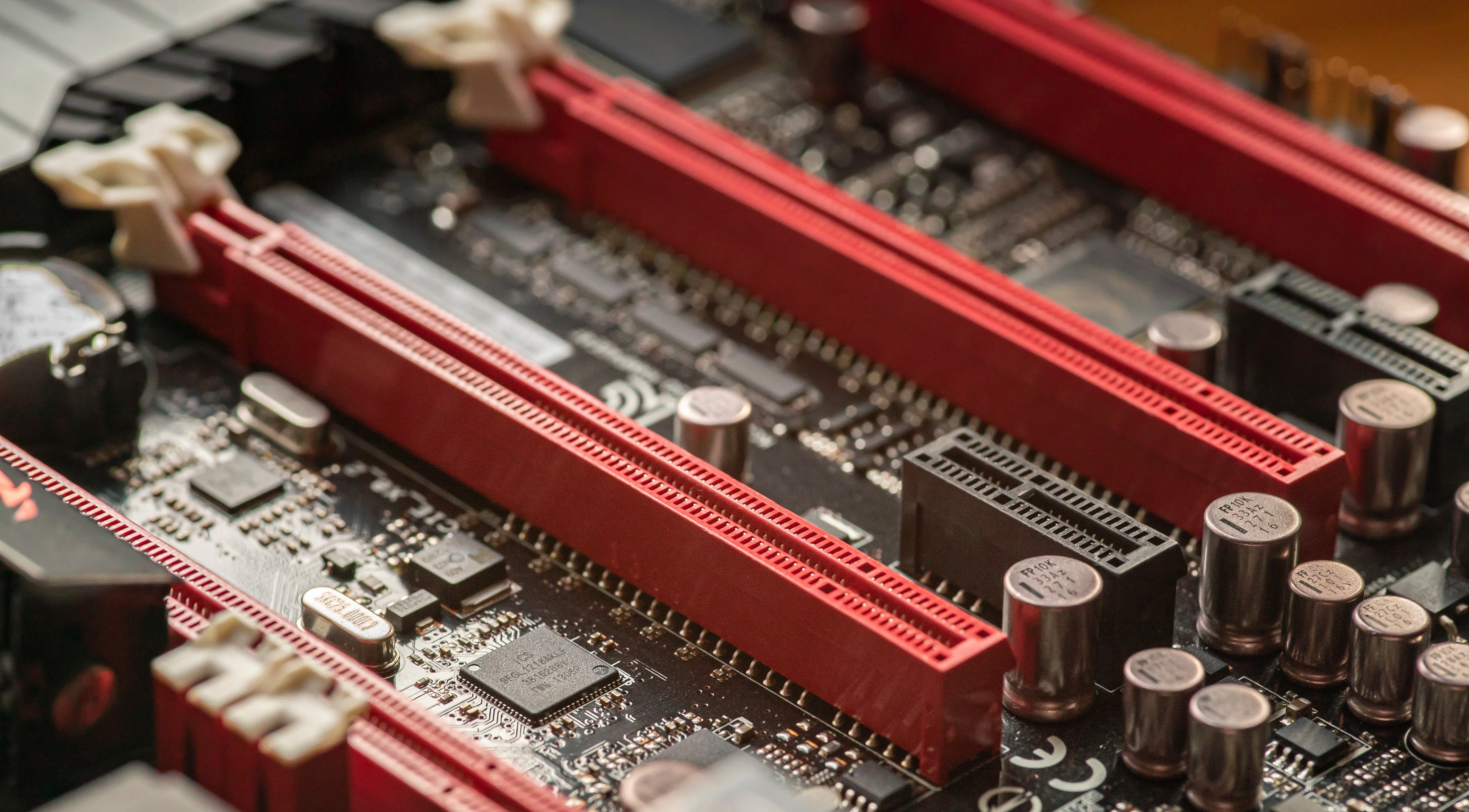
A PCIe connector, also known as a Peripheral Component Interconnect Express connector, is a type of expansion slot that allows various devices to be connected to a computer’s motherboard. It is primarily used to connect high-speed devices such as graphics cards, network cards, and storage devices to the motherboard.
Unlike its predecessor, PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) slots, PCIe connectors offer faster data transfer rates and more bandwidth. This makes them ideal for demanding applications that require high-speed data transfer and low-latency connections.
PCIe connectors come in different sizes and versions, ranging from x1 to x32. The number represents the number of lanes available for data transfer, with x1 being the smallest and x32 being the largest. Each lane consists of two pairs of wires for transmitting and receiving data.
These connectors are typically found on desktop computers, servers, and workstation motherboards. They are identified by their distinct physical appearance, with notches and pins that align with the corresponding slot on the motherboard.
It’s important to note that PCIe connectors are not compatible with other expansion slot types, such as PCI or AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port). Therefore, it’s crucial to ensure compatibility between the device and the available PCIe slots on the motherboard.
Overall, PCIe connectors have revolutionized the way devices communicate with the motherboard, offering higher speeds, greater bandwidth, and improved performance. They have become the standard for connecting expansion cards and peripherals and continue to evolve to meet the demands of modern computing.
Definition of a PCIe Connector
A PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) connector is a type of interface that is used to connect expansion cards to a computer’s motherboard. It is a high-speed serial connection that allows for the transfer of data between the expansion card and the motherboard at a much faster rate than traditional PCI connectors.
The PCIe connector is designed to provide a faster and more efficient way to connect expansion cards such as graphics cards, network adapters, and sound cards to a computer system. It is commonly found in desktop computers, servers, and other devices that require high-speed data transfer.
The PCIe connector consists of a series of electrical contacts or pins that are arranged in a specific pattern. These contacts provide a physical connection between the expansion card and the motherboard, allowing for the transfer of both data and power.
One of the key features of the PCIe connector is its scalability. It allows for multiple lanes or channels to be used simultaneously, increasing the overall data transfer speed. A PCIe connector can have different numbers of lanes, such as x1, x4, x8, or x16, with x16 being the most common for high-performance graphics cards.
Moreover, the PCIe connector also supports hot-plugging, which means that the expansion card can be inserted or removed from the connector while the computer is powered on. This eliminates the need to shut down the system when adding or replacing an expansion card, making it more convenient and efficient.
Types of PCIe Connectors
PCIe connectors come in various types, each designed to meet specific requirements and accommodate different devices. Here are some of the most common types of PCIe connectors:
1. PCIe x1: This is the most basic form of PCIe connector, with a single lane. It is primarily used for low-bandwidth devices such as sound cards, network adapters, and USB expansion cards.
2. PCIe x4: This connector has four lanes and offers higher bandwidth compared to PCIe x1. It is commonly used for devices that require faster data transfer rates, such as RAID controllers, solid-state drives (SSDs), and some graphics cards.
3. PCIe x8: This connector has eight lanes and provides even greater bandwidth than PCIe x4. It is suitable for high-performance devices like high-end graphics cards, professional video editing cards, and advanced networking cards.
4. PCIe x16: This is the highest capacity PCIe connector, with sixteen lanes. It delivers the maximum bandwidth and is the most commonly used connector for high-end graphics cards, gaming GPUs, and other bandwidth-intensive devices.
5. M.2 PCIe: This is a smaller form factor PCIe connector designed primarily for ultra-thin laptops and small form factor desktops. M.2 PCIe connectors are commonly used for SSDs, Wi-Fi cards, and other compact peripheral devices.
6. Mini PCIe: This smaller form factor PCIe connector is commonly found in laptops and small embedded systems. It is used for various expansion cards, including wireless network cards, GPS modules, and modems.
7. U.2: Also known as SFF-8639, the U.2 connector is primarily used for high-performance SSDs. It provides a high-speed interface for enterprise-grade storage devices and offers faster data transfer rates compared to SATA-based connections.
Each PCIe connector type has its own specific use case and compatibility requirements. It is important to ensure that your device and motherboard support the desired PCIe connector type before purchasing or installing any expansion cards or peripherals.
Functions of a PCIe Connector
A PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) connector serves several important functions in a computer system. Let’s explore the key functions of a PCIe connector:
1. Data Transmission: The primary function of a PCIe connector is to provide a high-speed data transmission pathway between different components of a computer system. It allows the transfer of data between the motherboard and expansion cards such as graphics cards, sound cards, and network adapters. PCIe connectors offer significantly faster data transfer rates compared to older interface technologies such as PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) and AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port).
2. Expansion Capability: PCIe connectors allow users to expand the functionality of their computer systems by adding additional components. These connectors provide a standardized interface for connecting expansion cards, which can enhance the performance and capabilities of the system. Common expansion cards that use PCIe connectors include graphics cards for improved gaming and multimedia experiences, sound cards for enhanced audio quality, and RAID controllers for data storage management.
3. Power Delivery: In addition to data transmission, PCIe connectors also serve as a power delivery mechanism for connected components. PCIe slots provide electrical power to the expansion cards, eliminating the need for separate power connectors for each card. This simplifies the installation process and helps maintain a neat and organized system setup.
4. Hot-Swap Capability: Another important function of PCIe connectors is their ability to support hot-swapping. This means that expansion cards can be added or removed from the system while it is still running, without the need to shut down or restart the computer. This feature allows for convenient upgrades, replacements, and troubleshooting without interrupting the workflow or causing system downtime.
5. Backward Compatibility: PCIe connectors are designed to be backward compatible, allowing older expansion cards to be used with newer systems. This ensures that users can still utilize their existing hardware investments even as they upgrade to the latest computer systems with PCIe support. The backward compatibility feature provides flexibility and cost-effectiveness for users.
Common Uses of PCIe Connectors
PCIe connectors are widely used in various industries and applications due to their high-speed data transfer capabilities and versatility. Here are some common uses of PCIe connectors:
1. Gaming: PCIe connectors are commonly used in gaming PCs and consoles to provide high-speed connectivity for graphics cards. With the increasing demand for realistic graphics and smooth gameplay, PCIe connectors enable gamers to experience the latest gaming technologies.
2. Data Storage: PCIe connectors are utilized in storage devices such as solid-state drives (SSDs) and RAID controllers. These connectors enable faster data transfer rates, allowing for efficient data storage and retrieval processes. This is especially crucial in industries where handling large amounts of data in real-time is paramount.
3. Networking: PCIe connectors play a vital role in network interface cards (NICs) used for wired and wireless communication. By connecting NICs to the motherboard through PCIe connectors, high-speed data transmission is achieved, ensuring seamless connectivity and efficient network performance.
4. Video Editing and Production: PCIe connectors are essential in video editing and production setups. Graphics cards equipped with PCIe connectors enable real-time rendering and editing of high-resolution videos. Whether it’s for professional video editing or content creation, PCIe connectors ensure smooth playback and fast rendering capabilities.
5. Medical Imaging: PCIe connectors are commonly found in medical imaging devices such as ultrasound systems, MRI scanners, and CT scanners. These connectors enable the transfer of large amounts of imaging data quickly and efficiently, allowing medical professionals to diagnose and treat patients effectively.
6. Industrial Automation: PCIe connectors are used in industrial automation systems to facilitate high-speed data communication between various components. Whether it’s control systems, sensors, or actuators, PCIe connectors ensure reliable and efficient data transfer, enhancing overall system performance.
7. High-Performance Computing: PCIe connectors are integral in high-performance computing (HPC) applications, such as supercomputers and advanced scientific research. By connecting high-performance GPUs, FPGAs, or other accelerators, PCIe connectors enable parallel processing and data-intensive calculations, pushing the boundaries of computational power.
Overall, PCIe connectors have become indispensable in a wide range of industries and applications. Their ability to provide high-speed, reliable connectivity makes them the go-to choice for demanding tasks that require fast data transfer rates and real-time processing capabilities. As technology continues to advance, PCIe connectors will continue to evolve and adapt to meet the ever-growing demands of the digital world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the role and importance of a PCIe connector is crucial for anyone in the field of computer hardware and technology. The PCIe connector serves as the primary interface for connecting expansion cards to a computer’s motherboard and facilitates high-speed data transfer between the various components of a system. By utilizing this standardized interface, users can upgrade and expand their computer’s capabilities with ease.
Whether it’s for gaming, video editing, or any other demanding tasks, having a reliable PCIe connector ensures optimal performance and compatibility. The advancements in PCIe technology have led to faster data transfer rates, enhanced power delivery, and improved efficiency. Therefore, it’s essential to choose the right PCIe connector that aligns with the specific requirements of your system.
With the knowledge gained from this article, you are now equipped to make informed decisions when it comes to selecting and using PCIe connectors. So, go ahead, explore the world of PCIe, and unlock the full potential of your computer system.
FAQs
1. What is a PCIe connector?
A PCIe connector, also known as a PCI Express connector, is a high-speed serial interface used in computer systems to connect various peripherals and expansion cards to the motherboard. It provides a faster and more efficient data transfer rate compared to older connection standards like PCI and AGP.
2. What are the different types of PCIe connectors?
There are several types of PCIe connectors available, including PCIe x1, PCIe x4, PCIe x8, and PCIe x16. The number represents the number of “lanes” or data transfer paths available in each connector, with x1 having one lane and x16 having 16 lanes. The different types of PCIe connectors are designed to accommodate different expansion cards and their bandwidth requirements.
3. How do I identify a PCIe connector on my motherboard?
PCIe connectors on motherboards are usually distinguishable by their size and shape. They are typically longer than other connectors, such as PCI or AGP slots, and have a different configuration of pins. The number of pins in a PCIe connector can vary based on its type, with x1 connectors having fewer pins compared to the larger x16 connectors. Consult your motherboard’s manual or manufacturer’s website for specific information on identifying PCIe connectors.
4. What devices can be connected to a PCIe connector?
PCIe connectors are primarily used to connect expansion cards to a computer’s motherboard. These expansion cards can include graphics cards, network cards, sound cards, USB cards, and storage controllers, among others. Each type of expansion card requires a specific PCIe connector type, such as an x16 connector for high-end graphics cards or an x1 connector for network or sound cards.
5. Can I use a PCIe x16 card in a PCIe x8 slot?
In most cases, yes, you can use a PCIe x16 card in a PCIe x8 slot. PCIe slots are designed to be backward-compatible, meaning that a larger PCIe card can be used in a smaller PCIe slot. However, the card will only be able to utilize the available number of lanes. For example, if you install a PCIe x16 card in a PCIe x8 slot, it will only run at x8 speed instead of x16.
