When it comes to understanding the functionality of a MIDI connector, one common question that often arises is: which pin on a MIDI connector connects to ground? This is a crucial aspect to know, especially if you’re dealing with MIDI devices and accessories.
MIDI, short for Musical Instrument Digital Interface, is a widely-used protocol that allows electronic musical instruments, computers, and other devices to communicate and synchronize with each other. It uses a 5-pin DIN connector, with each pin serving a specific purpose in the MIDI signal transmission.
So, if you’re curious to learn about the ground pin on a MIDI connector and its significance, you’re in the right place. In this article, we’ll delve into the details of MIDI connectors, explore their pin configurations, and demystify the role of the ground pin in MIDI communication.
Inside This Article
- Explanation of MIDI Connectors
- Importance of Ground Connection in MIDI
- Pinout of MIDI Connectors
- Identifying the Ground Pin
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Explanation of MIDI Connectors
MIDI connectors are an essential component of the MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) system, which is used to connect musical instruments, computers, and other devices together to communicate and transmit musical data. These connectors facilitate the transfer of MIDI signals, allowing for seamless integration and control of multiple devices in a music production or performance setup.
There are two main types of MIDI connectors: MIDI IN and MIDI OUT. The MIDI IN connector is used to receive MIDI data from an external device, while the MIDI OUT connector is used to send MIDI data to an external device. These connectors are typically found on MIDI keyboards, synthesizers, sound modules, and other MIDI-compatible equipment.
The MIDI connectors themselves come in different forms, including the classic 5-pin DIN connectors and the more modern USB connectors. The 5-pin DIN connectors were the original standard for MIDI connections and are still widely used today. They consist of five pins, each serving a specific purpose in transmitting MIDI data.
The USB connectors, on the other hand, provide a more convenient and versatile way of connecting MIDI devices to computers and other devices. They use a standard USB interface, allowing for plug-and-play functionality and eliminating the need for additional MIDI interfaces or adapters.
The MIDI connectors, regardless of their type, are crucial for establishing a seamless and reliable connection between MIDI devices. They ensure that MIDI data is transmitted accurately and efficiently, allowing musicians, producers, and performers to control and synchronize their equipment effectively.
In addition to the MIDI IN and OUT connectors, some MIDI devices also feature other connectors, such as MIDI THRU and MIDI SYNC. The MIDI THRU connector allows MIDI data to be passively “thru” the device to another MIDI device, without affecting the original MIDI data. This feature is handy for creating complex MIDI setups or chaining multiple devices together.
The MIDI SYNC connector, also known as the MIDI clock sync or MIDI timecode input, is used to synchronize MIDI devices to an external clock source. This is particularly useful in scenarios where precise timing and synchronization are required, such as in live performances or multi-device MIDI setups.
Overall, MIDI connectors play a crucial role in the world of music production and performance. They enable seamless communication between MIDI devices, allowing musicians and producers to harness the full potential of MIDI technology and create captivating musical compositions.
Importance of Ground Connection in MIDI
When it comes to MIDI connectors, the ground connection plays a crucial role in ensuring proper functionality and signal integrity. Grounding is essential for maintaining a stable reference voltage level and minimizing signal interference.
In a MIDI interface, the ground connection serves as a common reference point for both the MIDI devices and the connecting cables. It provides a stable voltage level against which the signal voltages can be measured accurately, allowing for reliable communication between devices.
Without a good ground connection, the MIDI signal can become distorted or weakened due to electrical noise. This noise can come from various sources, including electromagnetic interference from other cables or devices, power surges, or even internal circuitry noise within the MIDI devices themselves.
By providing a solid ground connection, the MIDI devices can effectively shield the signal from external interference and ensure that it reaches its destination intact. This is especially crucial in professional audio setups where signal quality and reliability are of utmost importance.
Furthermore, a proper ground connection helps prevent ground loops, which occur when there are multiple paths for electrical currents to flow through the ground. Ground loops can introduce unwanted hums, buzzes, or distortions in the audio signal, degrading the overall sound quality.
To avoid ground loop issues, it is essential to establish a single point of ground reference within the MIDI setup. This can be achieved by connecting all the MIDI devices and cables to a common ground point, usually provided by the MIDI interface or a dedicated ground connection.
Overall, the ground connection in MIDI is not something to overlook. It plays a critical role in maintaining signal integrity, minimizing interference, and ensuring high-quality audio transmission. So, whether you are a musician, producer, or audio enthusiast, paying attention to the grounding aspect of your MIDI setup can lead to a more reliable and pristine audio experience.
Pinout of MIDI Connectors
MIDI connectors are commonly used in music production and instrument setups to transmit musical data. The MIDI connector has a specific pinout configuration that determines the function of each pin. Understanding the pinout of MIDI connectors is crucial for connecting and configuring MIDI devices properly.
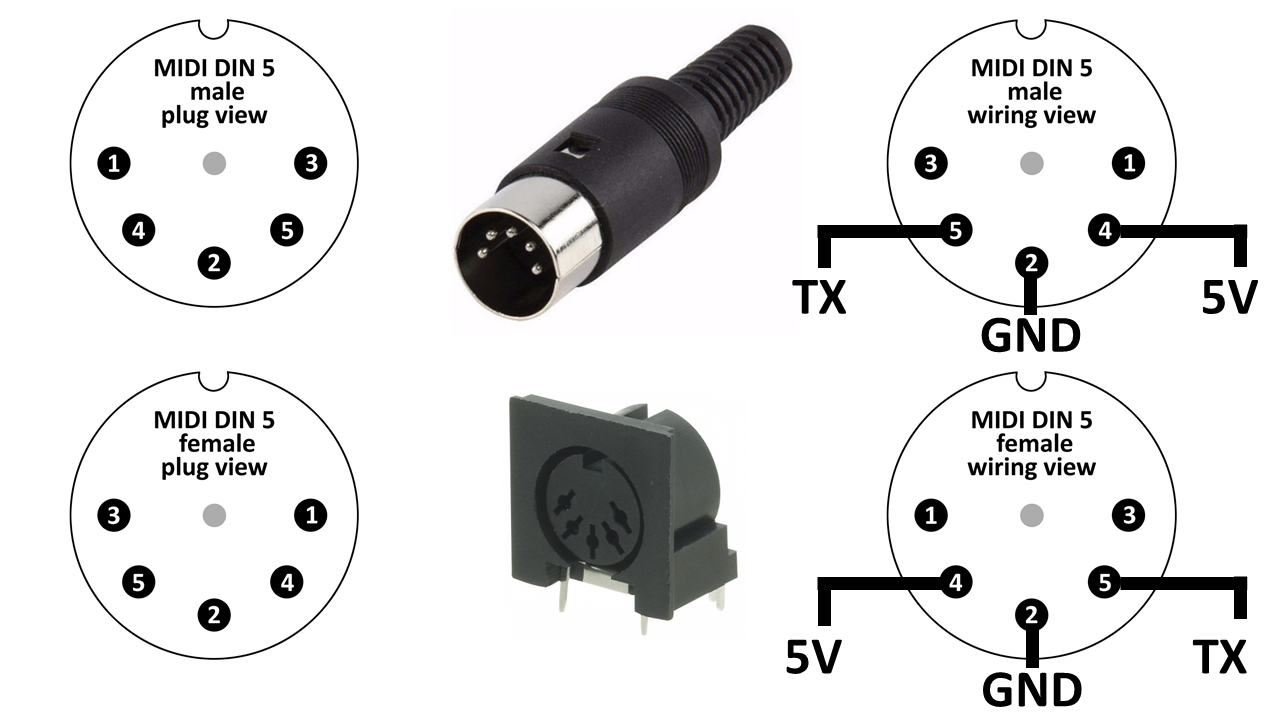
The MIDI connector primarily consists of a circular 5-pin DIN (Digital Interface Connector) design. This standard MIDI connector is known as a MIDI Type A connector. Each pin within the connector has a specific purpose and plays a vital role in transmitting MIDI data accurately.
Here is a breakdown of the pinout configuration of a standard MIDI connector:
- Pin 1: Shield/Earth Ground – This pin provides a connection to the electrical ground, ensuring proper grounding and reducing noise interference in the MIDI signal transmission.
- Pin 2: MIDI Data – This pin carries the MIDI data signal, which includes information about note events, control changes, and other musical information.
- Pin 3: MIDI Data – This pin also carries the MIDI data signal, acting as an alternate signal path for MIDI information.
- Pin 4: Not Connected – This pin is not used in the standard MIDI connector configuration and is left unconnected.
- Pin 5: +5V Power – This pin provides a +5V power supply for certain MIDI devices that require power through the MIDI connection.
It is important to note that the pin configuration of MIDI connectors may vary in other types of MIDI connectors, such as the smaller MIDI Type B connector or the MIDI Type C connector. However, the standard 5-pin DIN MIDI connector is the most commonly used and widely recognized.
When connecting MIDI devices, it is essential to ensure the proper alignment of the pins and a secure connection. Incorrectly connecting the MIDI cables can result in malfunctioning or unreliable MIDI communication between devices.
By understanding the pinout configuration of MIDI connectors, you can confidently connect and configure your MIDI devices, ensuring seamless communication and optimal performance in your music production or instrument setup.
Identifying the Ground Pin
When it comes to identifying the ground pin on a MIDI connector, it is essential to have a clear understanding of the pinout configuration. Usually, MIDI connectors feature a total of five pins, each serving a specific purpose in transmitting data between devices.
To determine which pin on a MIDI connector connects to ground, you can rely on the standard pinout convention. The ground pin is typically labeled with the symbol for ground, which is often represented by the letter ‘G’ or a simple horizontal line. This symbol indicates the reference point for the electrical signals flowing through the cable.
Another way to identify the ground pin is by examining the physical characteristics of the connector. In most cases, the ground pin is the one closest to the metal casing of the connector. It is often slightly larger or has a different shape than the other pins, making it easier to identify visually or by touch.
Additionally, if you have access to the MIDI manufacturer’s documentation or specifications, it will clarify which pin connects to ground. This resource will provide a detailed diagram or pinout information that leaves no room for uncertainty.
It’s important to be cautious when identifying the ground pin, especially if you plan to modify or build custom MIDI cables. Incorrectly identifying the ground pin can result in signal interference, data loss, or even damage to connected devices. If you are unsure or uncomfortable with the process, it is always advisable to consult with an experienced technician or refer to professional resources.
Remember, proper grounding is crucial for reliable and error-free MIDI communication. By correctly identifying and connecting the ground pin, you can ensure a stable electrical reference point for the MIDI signals, promoting optimal performance and reducing the risk of signal degradation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the different pins on a MIDI connector can greatly aid in troubleshooting and ensuring a proper connection. While the MIDI connector itself is a simple design, each pin serves a specific function, allowing for the seamless transmission of MIDI data between devices.
By knowing which pin connects to ground, you can identify and fix potential issues related to grounding problems in your MIDI setup. Grounding problems can cause unwanted noise, signal degradation, or even complete signal loss. Therefore, it is crucial to have a solid understanding of the grounding pin and its role in maintaining a reliable and high-quality MIDI connection.
Whether you’re a musician, a producer, or simply a MIDI enthusiast, having a grasp of the MIDI connector and its pin configuration is essential. This knowledge will ensure smooth communication between your MIDI devices and a hassle-free experience when creating music or using MIDI-controlled equipment.
FAQs
Q: Which pin on a MIDI connector connects to ground?
A: In a standard 5-pin MIDI connector, pin 2 is the ground connection. It ensures proper electrical grounding and helps eliminate noise interference in MIDI signals.
Q: How do I identify the ground pin on a MIDI connector?
A: The ground pin on a MIDI connector is usually the second pin from the left when looking at the front of the connector, with the orientation notch facing upwards. It is color-coded black and is labeled as “GND” on most MIDI connectors.
Q: Why is the ground connection important in a MIDI connector?
A: The ground connection in a MIDI connector is crucial for maintaining signal integrity and preventing noise interference. It provides a reference point for the electrical signals, ensuring accurate and reliable transmission of MIDI data.
Q: Are all MIDI connectors standardized with the ground pin in the same position?
A: Yes, the MIDI standard specifies that pin 2 is the ground connection on a 5-pin MIDI connector. This standardization ensures compatibility between MIDI devices from different manufacturers.
Q: Can I use a MIDI connector without connecting the ground pin?
A: It is not recommended to use a MIDI connector without connecting the ground pin. The ground connection plays a critical role in maintaining proper signal integrity and reducing noise interference. Neglecting to connect the ground pin can result in unstable or unreliable MIDI data transmission.
