Have you ever wondered how a touchscreen on your mobile device actually works? It may seem like magic, but in reality, it’s a fascinating blend of technology and engineering. Touchscreens have become an integral part of our daily lives, allowing us to interact with our phones, tablets, and other devices effortlessly. By understanding the underlying principles behind touchscreen technology, we can appreciate the incredible convenience and functionality these devices provide. In this article, we will delve into the inner workings of touchscreens, exploring the different types, how they detect touch, and the technologies used to make them responsive. So, let’s dive in and unravel the mystery behind how touchscreens work!
Inside This Article
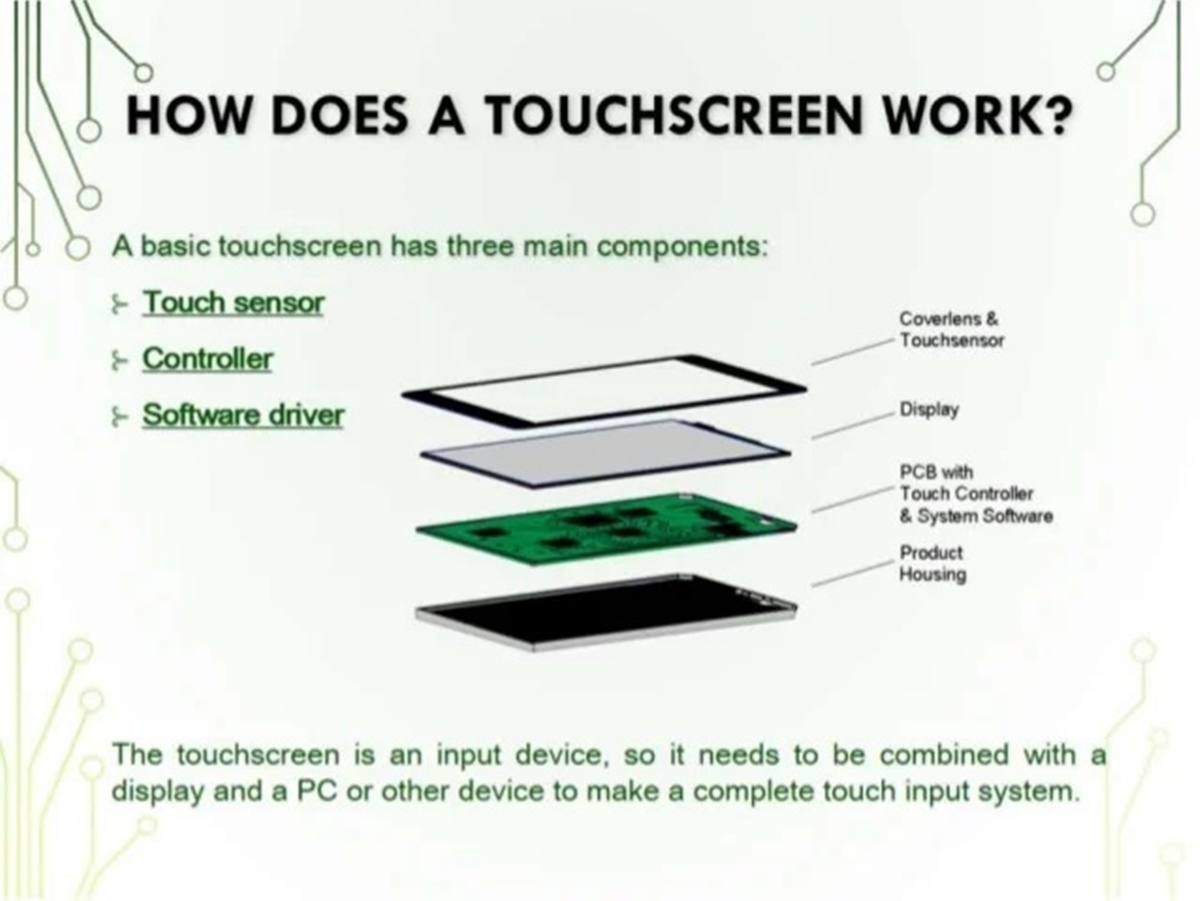
- Understanding Touchscreens – Definition of a Touchscreen – Capacitive vs. Resistive Touchscreens
- Components of a Touchscreen- Touch Sensor- Controller- Display
- How Touchscreens Work- The Principle of Electric Conductivity- Touchscreen Technology: Capacitive and Resistive- Touch Detection and Localization
- Capacitive Touchscreens
- Resistive Touchscreens: Resistive Touch Technology, Single-touch Functionality, Common Applications
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Understanding Touchscreens – Definition of a Touchscreen – Capacitive vs. Resistive Touchscreens
When it comes to mobile accessories, touchscreens play a crucial role in enabling user interaction and enhancing the overall user experience. In this article, we will delve into the world of touchscreens, starting with understanding their basic definition and exploring the key differences between two popular types: capacitive and resistive touchscreens.
A touchscreen is a display panel that responds to the touch of a user’s finger or a stylus. It serves as an input medium, allowing users to interact directly with the device without the need for a physical keyboard or mouse. This technology has revolutionized the way we interact with our smartphones, tablets, and other electronic devices.
Now, let’s explore the two main types of touchscreens: capacitive and resistive.
Capacitive Touchscreens
Capacitive touchscreens are the most widely used touch technology in modern mobile devices. These touchscreens utilize the electrical properties of the human body to detect and respond to touch. They consist of a glass panel coated with a transparent conductive material, typically indium tin oxide (ITO).
Capacitive touchscreens work by sensing the changes in electrical current when a conductive object, such as a finger, touches the screen. The screen’s controller measures the electrical charge at various points on the touchscreen to determine the touch location. This method allows for precise and multi-touch input, enabling gestures like pinch-to-zoom and swipe.
Capacitive touchscreens offer several advantages, including excellent responsiveness, high clarity, and durability. They are ideal for applications that require precise touch input and multi-touch capabilities, such as gaming, web browsing, and typing.
Resistive Touchscreens
Resistive touchscreens are another type of touchscreen technology commonly found in older mobile devices and industrial applications. These touchscreens consist of multiple layers, including two flexible layers with a gap between them. The layers are made of a conductive material such as indium tin oxide (ITO) or a composite of polyester and glass.
When pressure is applied to the outer layer of a resistive touchscreen, it comes into contact with the inner layer, completing an electrical circuit. The controller then determines the touch position by measuring the change in voltage along the X and Y axes.
Resistive touchscreens offer a few advantages, such as durability and compatibility with gloves and stylus input. However, they are less responsive compared to capacitive touchscreens and do not support multi-touch gestures.
In summary, capacitive touchscreens provide a more advanced and intuitive user experience with their precise touch recognition and multi-touch capabilities. On the other hand, resistive touchscreens are more suitable for specific applications where glove or stylus input is required.
Now that we have a basic understanding of touchscreens and the differences between capacitive and resistive technologies, let’s take a closer look at the components that make up these touchscreens and how they work together.
Components of a Touchscreen- Touch Sensor- Controller- Display
A touchscreen is a modern input device that enables users to interact with electronic devices by directly touching the screen. It has revolutionized the way we interact with smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices. A touchscreen consists of several key components that work together seamlessly to provide a smooth and responsive user experience. Let’s take a closer look at the three primary components of a touchscreen: the touch sensor, the controller, and the display.
The touch sensor is a crucial component of a touchscreen. It is responsible for detecting and translating touch inputs into electrical signals that the device can understand. There are different types of touch sensors used in touchscreens, such as capacitive and resistive. Capacitive touch sensors are the most common and widely used in modern touchscreens. They rely on the electrical properties of the human body to detect touch inputs. Resistive touch sensors, on the other hand, use pressure to detect touch inputs.
The controller is the brain of the touchscreen. It processes the electrical signals received from the touch sensor and communicates with the device’s operating system to execute the appropriate commands. The controller ensures accurate and precise touch detection, allowing users to interact with the device effortlessly. It also manages other features of the touchscreen, such as multi-touch functionality and gesture recognition.
The display is the final component of a touchscreen. It is responsible for presenting the visual output to the user based on their touch inputs. The display technology used in touchscreens can vary, ranging from LCD to OLED and AMOLED. These display technologies provide vibrant and sharp images, enhancing the overall user experience. The display must be responsive and capable of registering touch inputs accurately to provide a seamless user interaction.
How Touchscreens Work- The Principle of Electric Conductivity- Touchscreen Technology: Capacitive and Resistive- Touch Detection and Localization
Touchscreens have become an essential part of our daily lives, allowing us to interact with our devices in a more intuitive and efficient manner. But have you ever wondered how touchscreens actually work? In this section, we will explore the principle of electric conductivity, the two main touchscreen technologies – capacitive and resistive, and touch detection and localization.
At the heart of touchscreens lies the principle of electric conductivity. When you touch the screen, your body’s natural electric conductivity allows the touchscreen to detect the interaction. It’s similar to how static electricity can be discharged when you touch a metal object.
There are two main types of touchscreen technology: capacitive and resistive. Capacitive touchscreens use a layer of capacitive material, typically indium tin oxide (ITO), which can hold an electrical charge. When you touch the screen, your finger’s electrical charge disrupts the screen’s electrostatic field, allowing the touchscreen to detect the touch.
On the other hand, resistive touchscreens consist of multiple layers, including a flexible top layer and a rigid bottom layer, separated by tiny insulating dots. When you touch the screen, pressure causes the top layer to come into contact with the bottom layer, completing a circuit and triggering touch detection.
Touch detection and localization are vital aspects of touchscreen technology. In capacitive touchscreens, a network of electrodes is located along the edges of the screen. When you touch the screen, the disruption in the electrostatic field is analyzed to precisely locate the touch point. This technology enables multi-touch functionality, allowing for gestures like pinch-to-zoom and swipe.
Resistive touchscreens, on the other hand, detect touch through pressure. When you touch the screen with sufficient pressure, the top and bottom layers make contact at that specific point, and the circuit is completed. However, resistive touchscreens typically support single-touch functionality only.
Touchscreens have a wide range of applications, from smartphones and tablets to self-service kiosks and industrial control panels. Their versatility and ease of use have revolutionized the way we interact with technology, making them an essential component of modern devices.
Capacitive Touchscreens
Capacitive touchscreens are one of the most popular touch technologies used in mobile devices and other electronic devices. Unlike resistive touchscreens that rely on physical pressure, capacitive touchscreens work by sensing the electrical properties of the human body.
Capacitive touch technology is based on the principle of capacitance. The surface of a capacitive touchscreen is coated with a transparent conductor like indium tin oxide (ITO). When a user touches the screen, it creates a change in capacitance due to the body’s conductive properties.
One key advantage of capacitive touchscreens is their ability to support multi-touch functionality. This means that the screen can detect and respond to multiple simultaneous touches, allowing for gestures like pinch-to-zoom and two-finger scrolling.
Capacitive touchscreens have become increasingly common in smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices. Their smooth and responsive nature makes them ideal for tasks that require precise control and gesture-based interactions.
In addition to portable devices, capacitive touchscreens are also used in various other applications, such as information kiosks, touch-enabled monitors, and automotive displays. They provide a user-friendly and intuitive interface for interacting with digital content.
Resistive Touchscreens: Resistive Touch Technology, Single-touch Functionality, Common Applications
Resistive touchscreens are a popular type of touch technology that allow users to interact with devices by applying pressure to the screen. This technology uses layers of conductive materials to detect touch input and enable the desired actions.
The resistive touch technology consists of two main layers: a resistive layer and a flexible layer. The resistive layer is made up of a thin film that has a conductive surface. The flexible layer, typically made of polyester, is placed on top and has a conductive coating on its underside.
When a user touches the screen, the pressure causes the two layers to make contact at the exact location. This completes a circuit and sends a signal to the controller, which then translates the touch into a specific action.
Unlike capacitive touchscreens, resistive touchscreens offer single-touch functionality, meaning they can detect and respond to only one point of contact at a time. This limitation makes them less suitable for complex multi-touch gestures but still highly effective for simple interactions.
Resistive touchscreens find applications in various industries and devices. They are commonly used in point-of-sale systems, where users need to input numeric data or make simple selections. Resistive touchscreens are also found in industrial equipment, medical devices, and handheld GPS devices.
While resistive touchscreens may not offer the advanced features of capacitive touchscreens, they are known for their durability and ability to function even when touched with a stylus, gloved hands, or other objects. This versatility makes resistive touch technology a reliable and cost-effective solution for many applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, touchscreens have revolutionized the way we interact with our devices, providing a seamless and intuitive user experience. By understanding how touchscreens work, we can appreciate the intricate technology behind them. Through a combination of capacitive or resistive touch panels, touch controllers, processors, and software algorithms, touchscreens are able to detect our touch gestures and translate them into commands.
As touchscreens continue to evolve, we can expect even more advanced features and functionalities, such as multi-touch, pressure sensitivity, and haptic feedback. The versatility of touchscreen technology has made it an essential component of our daily lives, incorporated not only in smartphones and tablets but also in a wide range of devices, from laptops to smartwatches to kitchen appliances.
Whether it’s tapping, swiping, or pinching, touchscreens have become an integral part of our modern society. Their convenience, effectiveness, and accessibility have made them a cornerstone of mobile technology. So the next time you use your smartphone or tablet, take a moment to appreciate the wonders of touchscreen technology that have brought about a whole new level of interaction and convenience.
FAQs
1. How does a touchscreen work?
A touchscreen is a display technology that allows users to interact with electronic devices by directly touching the screen. The screen is made up of multiple layers, including a bottom layer that contains an electrical current. When you touch the screen, it disrupts this current, and the device detects the change in electrical flow. This information is then processed by the device’s software, allowing it to determine the precise location of the touch and perform the corresponding action.
2. Are all touchscreens the same?
No, not all touchscreens are the same. There are different types of touchscreen technologies, including resistive, capacitive, and infrared. Each technology has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. For example, resistive touchscreens are pressure-sensitive and can be operated with gloves or stylus, while capacitive touchscreens are more responsive and require a conductive touch, like that of a human finger.
3. Can touchscreens work with any object?
Touchscreens are designed to work with specific objects, mainly conductive objects like a finger or a stylus specifically designed for touchscreen use. Common objects like pens, pencils, or regular gloves may not be recognized by most touchscreens, as they lack conductivity. However, there are specialized touchscreens that can detect certain objects, such as a gloved hand or even a gloved finger with a capacitance tip.
4. How do multi-touch gestures work on touchscreens?
Multi-touch gestures on touchscreens allow users to interact with the device using more than one finger at a time. This functionality is achieved through the use of capacitive touchscreens that can detect the simultaneous touch of multiple fingers. The touch controller in the device analyzes the different touch points and translates them into specific gestures, such as pinch-to-zoom or swipe gestures.
5. What are the advantages of using a touchscreen device?
There are several advantages to using a touchscreen device. Firstly, touchscreens offer a more intuitive and direct way of interacting with electronic devices, eliminating the need for physical keyboards or mice. They also provide a more immersive and interactive user experience. Additionally, touchscreens allow for quicker navigation through menus and options, making tasks more efficient. They are also more accessible for individuals with limited dexterity or physical disabilities, as they can be operated with just a touch.
