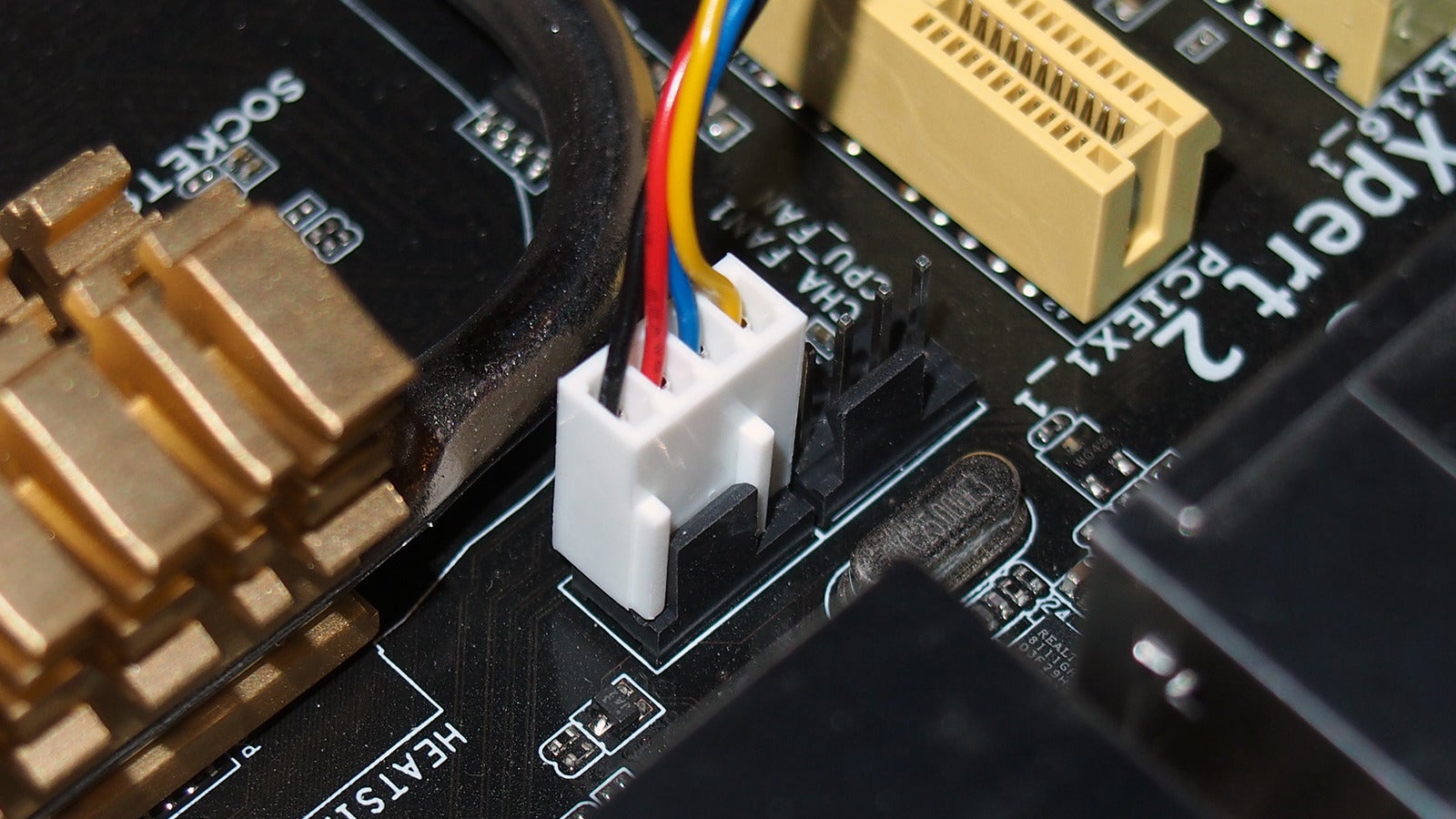
When it comes to the internal components of a computer, the motherboard is undeniably one of the most crucial elements. It acts as the central hub, connecting all the different parts together. But have you ever wondered about those tiny pins on the motherboard’s fan connector? In particular, what information does the fourth pin provide? In this article, we will delve into the world of motherboard fan connectors and explore the purpose and significance of the fourth pin. Understanding this pin’s function is essential for optimizing the performance and cooling capabilities of your computer. So, let’s unravel the mystery surrounding the fourth pin on a motherboard fan connector and shed light on its importance in maintaining the overall health and efficiency of your system.
Inside This Article
- Overview of Motherboard Fan Connectors
- The Purpose of the Fourth Pin on a Motherboard Fan Connector
- Functions and Information Provided by the Fourth Pin
- Common Uses and Configurations of the Fourth Pin On a Motherboard Fan Connector
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Overview of Motherboard Fan Connectors
Motherboard fan connectors are essential components in a computer system that allow users to connect fans to the motherboard. These connectors provide power and control signals to the fans, enabling them to efficiently cool down the system by dissipating heat. Understanding the different types of fan connectors and their functionalities is important for proper setup and optimization of the cooling system.
Modern motherboards typically feature multiple fan connectors, each with its own purpose and specifications. The most common type of fan connector found on motherboards is the 3-pin connector. It provides basic functionality, allowing the fan to receive power from the motherboard and run at a fixed speed. However, modern motherboards also come equipped with 4-pin connectors, which offer additional features and control options.
The 4-pin fan connector, also known as the PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) connector, provides the same power as a 3-pin connector but introduces more advanced control capabilities. The extra pin on the 4-pin connector allows the motherboard to regulate the fan speed dynamically based on temperature and system demands. This dynamic control mechanism helps optimize cooling efficiency, reduce noise levels, and prolong the lifespan of the fan.
It’s important to note that 4-pin fan connectors are backward compatible with 3-pin fans. If you connect a 3-pin fan to a 4-pin connector, the fan will still receive power and operate properly, but it will not benefit from the dynamic speed control offered by the additional pin. Likewise, you can also connect a 4-pin fan to a 3-pin connector, but again, the fan will only run at a fixed speed.
Overall, motherboard fan connectors play a crucial role in maintaining the optimal temperature of a computer system. Whether you’re using a 3-pin or a 4-pin connector, it’s essential to ensure proper placement and configuration of fans to achieve efficient cooling and enhance the overall performance and longevity of your system.
The Purpose of the Fourth Pin on a Motherboard Fan Connector
When it comes to connecting fans to a motherboard, you may have noticed that most fans come with a four-pin connector. While the first three pins are pretty intuitive, providing power and ground connections, the purpose of the fourth pin might leave you wondering. Well, fret not! In this article, we will delve into the purpose of the fourth pin on a motherboard fan connector and discuss the functions and information it provides.
The fourth pin on a motherboard fan connector serves a crucial role in controlling the fan’s speed and monitoring its performance. This pin enables the motherboard to communicate with the fan, adjusting the fan’s speed according to the system’s needs, and gathering information about its operating conditions. In other words, it allows for dynamic control and monitoring of the fan’s operations.
One of the primary functions of the fourth pin is pulse width modulation (PWM). PWM is a technique used to control the power supplied to the fan, effectively adjusting its speed. By varying the width of the pulses sent through the fourth pin, the motherboard can regulate the voltage supplied to the fan, thereby controlling its rotational speed. This allows the system to maintain an optimal balance between cooling performance and noise levels.
In addition to PWM control, the fourth pin also provides crucial information about the fan’s speed. It utilizes a tachometer signal, which is feedback from the fan’s rotation. By receiving this signal, the motherboard can monitor the fan’s RPM (revolutions per minute). This RPM data can be vital for ensuring that the fan is functioning properly and alerting the system if there are any issues, such as a fan failure or an unusually low or high speed.
The fourth pin on a motherboard fan connector also enables additional functionality, such as fan speed profiles or fan speed control through software. Many modern motherboards offer convenient software interfaces through which users can customize their fan profiles, setting predefined parameters for different scenarios. This allows users to fine-tune their system’s cooling performance based on their specific requirements, whether it be performance-oriented tasks or noise reduction during idle periods.
Functions and Information Provided by the Fourth Pin
The fourth pin on a motherboard fan connector serves several important functions and provides essential information to ensure optimal performance. Let’s delve into the various functions and information provided by this pin:
1. PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) Control: One of the primary functions of the fourth pin is to provide PWM control for the connected fan. PWM control allows for precise regulation of fan speed, resulting in quieter operation and improved cooling efficiency. By varying the width of the electrical pulse applied to the fan, the fourth pin enables the motherboard to adjust the fan speed according to the system’s temperature demands.
2. Fan Speed Monitoring: Another crucial function of the fourth pin is to provide fan speed monitoring. This pin allows the motherboard to receive feedback on the actual rotational speed of the fan. By monitoring the fan speed, the system can detect abnormalities or malfunctions, ensuring that the fan operates within the desired range and effectively cools the system.
3. RPM (Revolutions Per Minute) Reporting: The fourth pin also provides information about the fan’s rotational speed through RPM reporting. The motherboard can retrieve this data and display it in the BIOS or software monitoring tools. RPM reporting allows users to monitor the fan’s performance and make adjustments if necessary, ensuring optimal cooling and preventing overheating.
4. Smart Fan Control: The fourth pin on a motherboard fan connector is often associated with smart fan control. Smart fan control features use sophisticated algorithms to dynamically adjust fan speed based on real-time temperature readings. This advanced control mechanism optimizes cooling performance while maintaining low noise levels, resulting in a more efficient and quieter system.
5. Power Delivery: In some cases, the fourth pin may also be responsible for providing power to the fan. While the primary purpose of the fourth pin is control and monitoring, it can also deliver a low amount of power to the fan motor, reducing the need for a separate power connector.
Overall, the fourth pin on a motherboard fan connector plays a crucial role in controlling, monitoring, and optimizing the performance of the connected fan. It ensures effective cooling, reduces noise, and provides essential feedback to maintain system health and stability.
Common Uses and Configurations of the Fourth Pin On a Motherboard Fan Connector
The fourth pin on a motherboard fan connector serves several important purposes, allowing for a range of common uses and configurations. Here are some of the most common uses and configurations of the fourth pin:
-
Speed Control: One of the primary uses of the fourth pin is to control the speed of the fan depending on the hardware and software settings. This allows for more precise control over the fan’s speed, enabling users to find the optimal balance between cooling performance and noise levels.
-
PWM Functionality: The fourth pin on a motherboard fan connector is often used to support Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) functionality. PWM allows for the fan speed to be adjusted by varying the input voltage. This provides greater control over the fan’s speed and can be particularly useful for managing temperature fluctuations and ensuring efficient cooling.
-
Tachometer Signal: Another important function of the fourth pin is to provide the motherboard with a tachometer signal. This signal allows the motherboard to monitor and display the fan speed in real-time, providing valuable information about the cooling performance of the system.
-
Automatic Fan Control: The fourth pin is crucial for implementing automatic fan control. By using the tachometer signal and in conjunction with motherboard software, the system can adjust the fan speed dynamically based on temperature readings. This ensures that the fan operates at the most appropriate speed to maintain optimal cooling without excessive noise.
-
Fan Failure Detection: The fourth pin on the motherboard fan connector can also be used to detect fan failure. By monitoring the tachometer signal, the system can detect when the fan stops spinning or malfunctions. This helps to prevent potential overheating issues by alerting the user or triggering an automatic shutdown to protect the hardware.
Overall, the fourth pin on a motherboard fan connector provides essential functionality for controlling and monitoring the fan’s speed, enabling automatic fan control, implementing PWM functionality, and detecting fan failure. These features are crucial for maintaining efficient cooling and protecting the system from potential damage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the fourth pin on a motherboard fan connector provides vital information for controlling and monitoring the speed and performance of the fan. This additional pin enables features such as pulse-width modulation (PWM) and allows for more precise control over the fan’s speed and responsiveness. By utilizing the information provided by the fourth pin, users can ensure efficient cooling, reduce noise levels, and extend the lifespan of their computer components.
FAQs
Q: What is the fourth pin on a motherboard fan connector for?
The fourth pin on a motherboard fan connector is typically used for Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) control. This allows the motherboard to regulate the speed of the fan, based on temperature fluctuations or user-defined settings. In simpler terms, the fourth pin enables the motherboard to adjust the fan speed dynamically, resulting in more efficient cooling and quieter operation.
Q: Can I use a three-pin fan on a four-pin motherboard fan connector?
Yes, you can use a three-pin fan on a four-pin motherboard fan connector. The three-pin fan will still function, but without PWM control. Instead, it will run at a fixed speed determined by the voltage supplied by the motherboard. Keep in mind that you may not have the flexibility to adjust the fan speed based on temperature changes or other variables.
Q: Are all motherboard fan connectors four-pin?
No, not all motherboard fan connectors are four-pin. While four-pin connectors are more common nowadays, you may come across older motherboards or budget-oriented models that have three-pin fan connectors. It’s important to check your motherboard’s specifications or user manual to determine the type of fan connectors it supports.
Q: Can I connect a four-pin fan to a three-pin motherboard fan connector?
Yes, you can connect a four-pin fan to a three-pin motherboard fan connector. The extra fourth pin on the fan connector is designed for PWM control, which won’t be utilized when connected to a three-pin connector. The fan will still function, but as mentioned earlier, you won’t have the ability to adjust its speed using PWM.
Q: How do I know if a fan is compatible with my motherboard?
To ensure compatibility between a fan and your motherboard, you need to consider two main factors: the physical connection type and the power requirements. Check whether your motherboard has the appropriate fan connector type (three-pin or four-pin) and ensure that the fan’s voltage and current requirements are within the limits specified by your motherboard. It’s always a good idea to consult your motherboard’s documentation or reach out to the manufacturer for further guidance if you’re uncertain.
