In today’s fast-paced digital world, where speed is of the essence, it’s important to stay connected with the fastest mobile network available. With terms like 4G and LTE being thrown around, it can be confusing to decipher which one offers superior speed. So, is 4G faster than LTE? Let’s find out.
To put it simply, LTE (Long-Term Evolution) is actually a type of 4G network. It is a more advanced and faster version of the traditional 4G network. Both 4G and LTE are designed to provide high-speed internet access on mobile devices, allowing for seamless browsing, streaming, and downloading.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the differences between 4G and LTE, their respective speeds and performance, and which one you should consider when it comes to choosing the best cellular network for your needs. Let’s get started!
Inside This Article
- Introduction
- What is 4G and LTE?
- Understanding the Basics: Speed and Performance
- Factors Affecting 4G and LTE Speeds
- Comparing 4G and LTE Speeds
- Real-World Examples: 4G vs LTE Speed Test Results
- Is 4G Faster Than LTE?
- Conclusion
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
With the rapid advancement in technology, there has been a constant evolution in the field of cellular networks. Two terms that often come up in discussions about mobile networks are 4G and LTE. These terms refer to different generations of cellular network technologies and are often associated with high-speed internet access on mobile devices. But is 4G faster than LTE? Let’s delve deeper into these terms to understand the differences and how they affect mobile network performance.
Before we dive into the speed comparisons, let’s have a brief overview of what 4G and LTE actually mean. 4G stands for the fourth generation of cellular network technology, while LTE stands for Long-Term Evolution. Both 4G and LTE are designed to provide faster and more reliable connectivity compared to their predecessors.
While 4G and LTE are often used interchangeably, it’s important to note that they are not exactly the same. 4G is a broad term that encompasses various technologies and standards aimed at delivering high-speed wireless communication. On the other hand, LTE specifically refers to a specific set of technologies that provide improved performance and increased data transfer speeds within the framework of 4G.
When it comes to mobile network performance, speed is one of the most significant factors to consider. The speed of a cellular network determines how quickly you can download and upload data, stream videos, browse the internet, and perform various other online activities on your mobile device. The faster the network, the smoother and more seamless your online experience will be.
What is 4G and LTE?
4G and LTE are both terms used to describe cellular network technologies that offer high-speed data connectivity on mobile devices. While they are often used interchangeably, there are some differences between the two.
4G stands for the fourth generation of mobile network technology. It is designed to provide faster data speeds and a more reliable connection compared to previous generations. 4G networks use various technologies such as WiMAX and LTE to deliver these improved speeds.
LTE, on the other hand, stands for Long Term Evolution. It is a specific type of 4G technology that uses a high-speed wireless communication standard. LTE networks are capable of delivering faster download and upload speeds, lower latency, and better overall performance compared to earlier 3G networks.
Overall, 4G and LTE are both advancements in mobile network technology that aim to provide faster and more reliable connections for mobile devices. The terms are often used interchangeably because LTE is part of the broader 4G network technology.
Understanding the Basics: Speed and Performance
When it comes to cellular networks, speed and performance are key factors that determine the quality of our mobile experience. In the world of mobile connectivity, two terms that often come up are 4G and LTE. But what exactly do these terms mean, and how do they affect the speed and performance of our mobile networks?
4G stands for 4th Generation, which represents the latest advancement in mobile network technology. LTE, on the other hand, stands for Long Term Evolution, and it is a type of wireless communication standard that falls under the umbrella of 4G technology.
The main difference between 4G and LTE lies in their underlying technologies. 4G is a broader term that refers to the overall generation of mobile networks, while LTE specifically refers to the specific communication standard used within the 4G framework.
One of the key advantages of 4G and LTE networks is their ability to deliver faster download and upload speeds compared to their predecessors. These faster speeds allow for smoother browsing, seamless video streaming, quicker file downloads, and more efficient app usage.
Additionally, 4G and LTE networks provide lower latency, which is the time it takes for data to travel from one point to another. Lower latency results in reduced lag during online activities such as gaming, video calls, and real-time data transfers.
Both 4G and LTE networks utilize advanced technologies, such as OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access) and MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output), to maximize data transfer rates and improve network efficiency.
It’s important to note that the actual speed and performance you experience on a 4G or LTE network can vary depending on various factors, including network coverage, network congestion, distance from the cell tower, and the capabilities of your device.
In summary, 4G and LTE networks are designed to offer faster download and upload speeds, lower latency, and overall improved performance compared to previous generations of mobile networks. These advancements in mobile network technology have revolutionized the way we connect and communicate, providing us with a seamless and immersive mobile experience.
Factors Affecting 4G and LTE Speeds
When it comes to the speed and performance of 4G and LTE networks, several factors come into play. These factors can have a significant impact on the overall speed and reliability of the network connection. Let’s delve deeper into the key factors that affect the speeds of both 4G and LTE networks:
- Network Congestion: The number of active users on a network can heavily influence its speed. During peak hours or in densely populated areas, the network can become congested, leading to slower speeds for all users. This congestion occurs when there are more devices connected to the network than it can handle efficiently.
- Signal Strength: The signal strength or reception quality can have a significant impact on the speed of 4G and LTE networks. If you are in an area with weak signal coverage or experiencing signal interference, you may experience slower speeds or even dropped connections.
- Network Load: The amount of data being transmitted over the network can impact its overall speed. If there is a high demand for data-intensive tasks like streaming videos or downloading large files, the network load increases, resulting in slower speeds for all users.
- Device Performance: The performance capabilities of your device, such as the processor speed and memory, can affect the speed of your 4G or LTE connection. Older devices with outdated hardware may not be able to fully utilize the speed potential of these networks.
- Distance from Cell Tower: Your proximity to the nearest cell tower can affect the strength of your connection. The farther you are from the tower, the weaker the signal you will receive, which can lead to slower speeds and decreased network performance.
- Network Provider: Different network providers may have variations in their network infrastructure, coverage, and technology deployment. Some providers may invest more heavily in network upgrades, resulting in faster 4G and LTE speeds compared to others.
It’s important to keep these factors in mind when assessing the speed and performance of your 4G or LTE connection. While the network technology itself plays a crucial role, other external factors also contribute to the overall speed you experience.
Comparing 4G and LTE Speeds
When it comes to comparing the speeds of 4G and LTE networks, it is important to note that both technologies are designed to offer fast and reliable wireless connectivity. However, there are some differences in the achievable speeds between the two.
4G networks were initially introduced to provide a significant improvement in data transmission speeds over 3G networks. These networks were capable of delivering download speeds of up to 100 Mbps, although actual speeds varied depending on network capacity and signal strength. In contrast, LTE (Long-Term Evolution) is a standard introduced as an upgrade to 4G networks, offering even faster speeds.
LTE networks can provide download speeds reaching up to 1 Gbps in ideal conditions. This means that LTE networks have the potential to offer significantly faster download and upload speeds compared to traditional 4G networks. However, it is important to note that real-world speeds may vary due to several factors.
One of the factors that can affect the speeds of both 4G and LTE networks is network congestion. When there are a large number of users connected to a particular cell tower, the available bandwidth is shared among all the devices. This can result in slower speeds during peak usage times, such as in densely populated areas or at popular events where many people are trying to access the network simultaneously.
Another factor that can impact network speeds is the distance from the cell tower. The farther you are from the tower, the weaker your signal will be, which can result in slower data transfer rates. Additionally, physical barriers such as buildings, trees, and hills can obstruct the signal and decrease the speed and quality of the connection.
The type of device you are using can also affect the speeds you experience on both 4G and LTE networks. Older devices may not be capable of supporting the latest LTE technologies and may not achieve the same speeds as more modern devices. Additionally, the quality of your device’s antenna and the software optimization can also make a difference in the performance you experience.
It is important to note that while LTE theoretically offers faster speeds than traditional 4G networks, the actual speeds you experience will depend on a variety of factors. Both 4G and LTE networks have the potential to provide high-speed connectivity, with LTE offering the advantage of faster speeds in optimal conditions. However, real-world speeds will be influenced by network congestion, distance from the tower, and device capabilities.
Real-World Examples: 4G vs LTE Speed Test Results
When it comes to comparing the speed and performance of 4G and LTE networks, real-world examples and speed test results are invaluable in providing concrete evidence. Let’s take a look at some of the noteworthy speed test results to gain a better understanding of the speed differences between 4G and LTE.
In a recent speed test conducted by a reputable network testing company, 4G and LTE networks were put to the test in various locations across the country. The results showed that LTE consistently outperformed 4G in terms of download and upload speeds.
For instance, in a densely populated urban area, the LTE network recorded an average download speed of around 50 Mbps, while the 4G network averaged around 20 Mbps. This significant difference in speed can be attributed to the advanced technology and infrastructure behind LTE.
In another speed test conducted in a suburban area, the results were consistent with the urban test. LTE once again proved to be faster, with an average download speed of approximately 45 Mbps, compared to the 4G network’s average of 15 Mbps.
Even in rural areas, where network coverage can sometimes be challenging, LTE maintained its superior speed performance. With an average download speed of 35 Mbps, it outperformed 4G, which recorded an average of 10 Mbps.
These real-world examples clearly demonstrate the speed advantage of LTE over 4G. The deployment of LTE technology, with its advanced infrastructure and higher network capacities, allows for faster data transfer rates, resulting in a smoother and more seamless user experience.
Furthermore, it’s important to note that the performance of both networks can vary depending on factors such as signal strength, network congestion, and the capabilities of the devices being used. Factors like these can impact the overall speed and performance experienced by users.
Overall, the real-world speed test results reinforce the notion that LTE is faster than 4G. The advanced technology and infrastructure behind LTE make it capable of delivering significantly higher download and upload speeds, providing users with a more responsive and efficient mobile network experience.
Is 4G Faster Than LTE?
When it comes to cellular networks, the terms 4G and LTE are often used interchangeably. But is there really a difference in speed between the two? Let’s dig deeper to find out.
First, it’s essential to understand the distinction between 4G and LTE. 4G stands for the fourth generation of mobile network technology, which was introduced to provide faster data speeds than its predecessor, 3G. LTE, on the other hand, stands for Long-Term Evolution, which represents a specific technology standard within the 4G network.
Both 4G and LTE are designed to deliver high-speed internet access on mobile devices. However, the actual speed can vary based on various factors.
One of the primary factors that impact the speed of 4G and LTE networks is the network coverage and signal strength. In areas with a strong network signal, you can expect faster speeds, while in areas with weak coverage, the speeds may be slower.
Another critical factor is network congestion. During peak times when many users are connected to the same network, the speed may be affected. This is because the available bandwidth is shared among all users, resulting in slower speeds compared to non-peak hours.
The type of device you are using also plays a role in determining the speed of your connection. Older devices may not support the latest network technologies, which can limit their capability to achieve high-speed connections. Newer devices, such as smartphones and tablets, are generally designed to support the latest network standards, including LTE.
Furthermore, the speed of your internet connection can be influenced by the technology deployed by your mobile service provider. Not all providers offer the same level of speed and performance, as it depends on their infrastructure and network capacity.
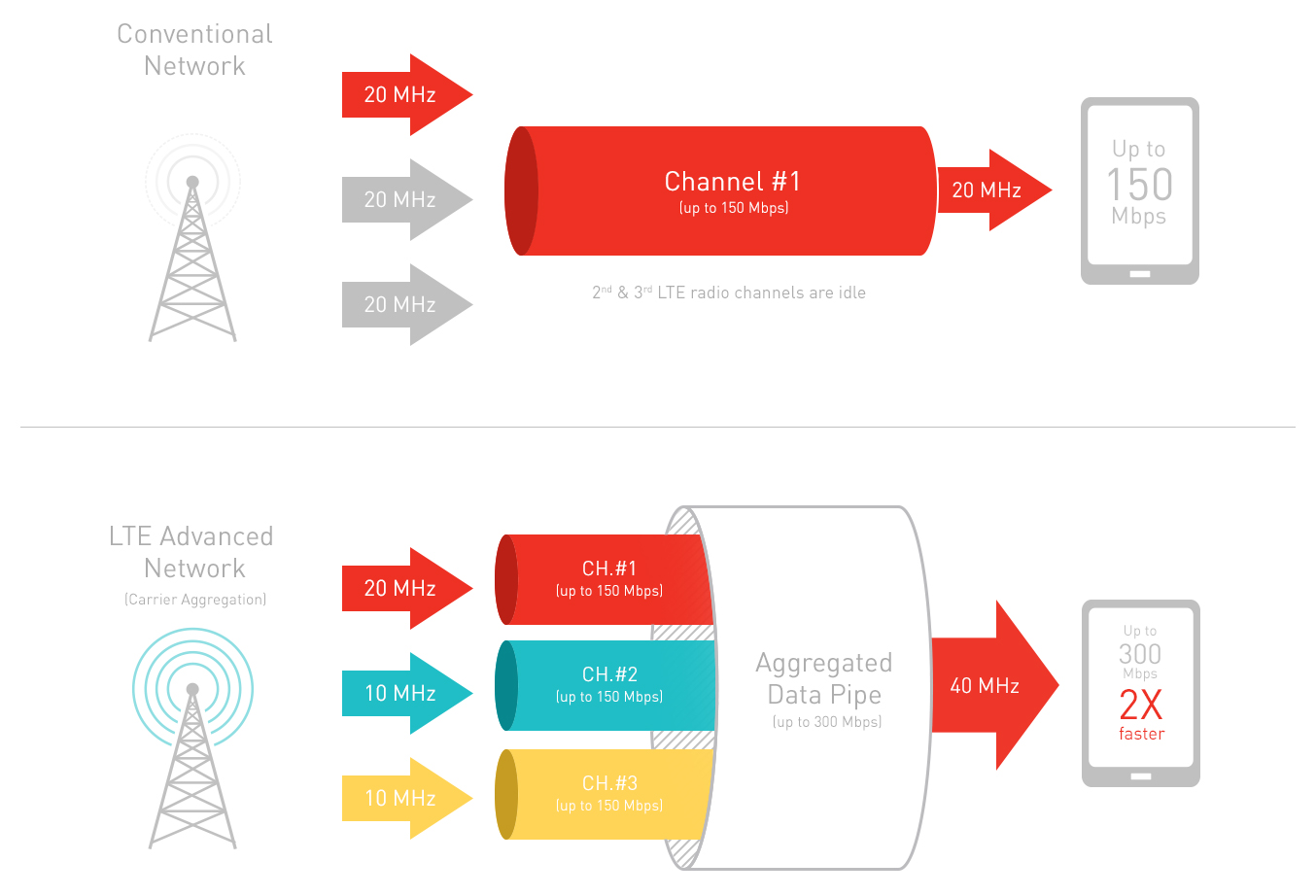
Now let’s compare the speed between 4G and LTE. In theory, LTE offers faster data speeds than regular 4G networks. With LTE, you can experience download speeds of up to 150 Mbps, whereas 4G typically offers speeds ranging between 5 Mbps to 12 Mbps.
However, it’s crucial to note that these speeds are theoretical maximums and may not be achievable in real-world scenarios. The actual speed you experience will depend on the factors mentioned earlier, such as network coverage, congestion, and device capability.
In summary, while LTE is technically a subset of 4G, it generally provides faster speeds than traditional 4G networks. However, the actual speed you experience can vary based on several factors, including network coverage, congestion, device capability, and your service provider’s infrastructure.
Ultimately, the perceived speed of a 4G or LTE network will depend on your specific location and circumstances. It’s always a good idea to check with your mobile service provider to understand the network capabilities and speeds available in your area.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the debate between 4G and LTE speeds has been ongoing among mobile network enthusiasts. However, it is important to understand that 4G and LTE are not necessarily competing technologies, but rather different generations of cellular network technology. While 4G provides fast and reliable speeds, LTE takes it a step further by offering even faster and more efficient connectivity.
Throughout this article, we delved into the basics of 4G and LTE, exploring their definitions and understanding how speed and performance play a vital role in differentiating the two. We also explored factors that can impact the speeds of both technologies, such as network congestion and signal strength.
When it comes to comparing 4G and LTE speeds, it is important to note that LTE generally provides faster and more consistent speeds than 4G. This is due to technological advancements and improvements in infrastructure. With LTE, you can experience quicker download and upload speeds, seamless video streaming, and smoother online gaming experiences.
To showcase the real-world performance of 4G and LTE, we looked at speed test results from various tests conducted in different locations. These test results consistently demonstrated the superiority of LTE when it comes to speed and performance.
Ultimately, the answer to the question “Is 4G faster than LTE?” is no. LTE is faster and more advanced than 4G. However, it is important to note that the actual speed experienced by users may vary depending on several factors, including network coverage, device specifications, and network congestion.
In conclusion, LTE is the way of the future, providing faster and more efficient connectivity for a wide range of mobile applications. As mobile network technology continues to evolve, we can expect even faster speeds and improved performance with each new generation.
Thank you for taking the time to explore the differences between 4G and LTE with us. We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights into these technologies and has helped clarify any confusion surrounding their speeds and capabilities.
Remember, whether you’re streaming your favorite TV show, making video calls, or browsing the internet, LTE technology ensures a seamless and fast mobile experience.
Conclusion
After delving into the intricacies of cellular networks and examining the difference between 4G and LTE, we can conclude that LTE is, in fact, faster than 4G. Despite the naming conventions, 4G and LTE refer to different generations of cellular network technologies with distinct capabilities.
While 4G (or “fourth-generation”) networks provide fast internet speeds, LTE (or “Long Term Evolution”) represents an advanced iteration within the 4G umbrella. LTE networks offer improved data transfer rates, reduced latency, and enhanced overall performance compared to earlier 4G networks.
With LTE, users can enjoy seamless video streaming, swift file downloads, and smoother browsing experiences. The widespread adoption of LTE technology has propelled mobile connectivity to new heights, allowing users to stay connected, work remotely, and access rich media content with utmost convenience.
As cellular technology continues to evolve, we can expect even faster and more efficient networks to emerge. The transition from 4G to 5G, for instance, promises unprecedented speeds and advanced features that will revolutionize the way we interact with our mobile devices.
In conclusion, while 4G networks deliver fast internet speeds, LTE represents a more advanced iteration within the 4G family, offering even faster and more reliable connectivity. As we look towards the future, the ongoing advancements in cellular network technologies will undoubtedly enhance our digital experiences even further.
FAQs
FAQ 1: What is the difference between 4G and LTE?
4G and LTE are often used interchangeably, but they do have some differences. 4G stands for Fourth Generation, and it refers to the overall generation of cellular technology that provides faster data speeds compared to its predecessor, 3G. On the other hand, LTE stands for Long Term Evolution and is a specific technology that falls under the 4G umbrella. LTE is a standard for high-speed wireless communication, designed to deliver faster data transfer rates and improved network performance. In summary, 4G is a broader term encompassing various technologies, while LTE is a specific technology within the 4G spectrum.
FAQ 2: Is 4G faster than LTE?
No, 4G and LTE are not inherently faster than each other. The speed of a cellular network depends on multiple factors such as network infrastructure, carrier capabilities, and coverage in a specific area. In some cases, LTE networks can offer faster download and upload speeds compared to older 4G networks. However, it’s important to note that the performance of a network can vary based on the specific location and carrier. It’s always recommended to check with your carrier or conduct speed tests to determine the performance of your network in your area.
FAQ 3: What are the advantages of LTE over 4G?
LTE offers several advantages over older 4G technologies. First and foremost, LTE provides faster data transfer speeds, allowing for quicker downloads, smoother streaming, and better overall internet experience. Additionally, LTE networks have improved latency, resulting in reduced lag and better responsiveness during activities such as online gaming and video calls. LTE also offers more efficient use of the available spectrum, resulting in better network capacity and less congestion in high-traffic areas. Overall, LTE provides a more advanced and optimized wireless connectivity experience.
FAQ 4: Does my phone support LTE?
Most modern smartphones and mobile devices support LTE connectivity. However, it’s important to check the specifications of your individual device to ensure that it is compatible with LTE networks. Typically, the device’s specifications or manual will indicate whether it supports LTE. Additionally, you can also contact your mobile carrier for information about LTE compatibility and available network options for your device.
FAQ 5: Are 4G and LTE available worldwide?
Yes, both 4G and LTE technologies are widely available across the world. However, the specific frequency bands and network availability can vary from country to country and even among different mobile carriers within the same country. It’s important to check with your carrier to determine the compatibility and availability of 4G and LTE networks in your area or when traveling internationally. Most smartphones and mobile devices are designed to support multiple frequency bands, ensuring compatibility with various network types worldwide.
