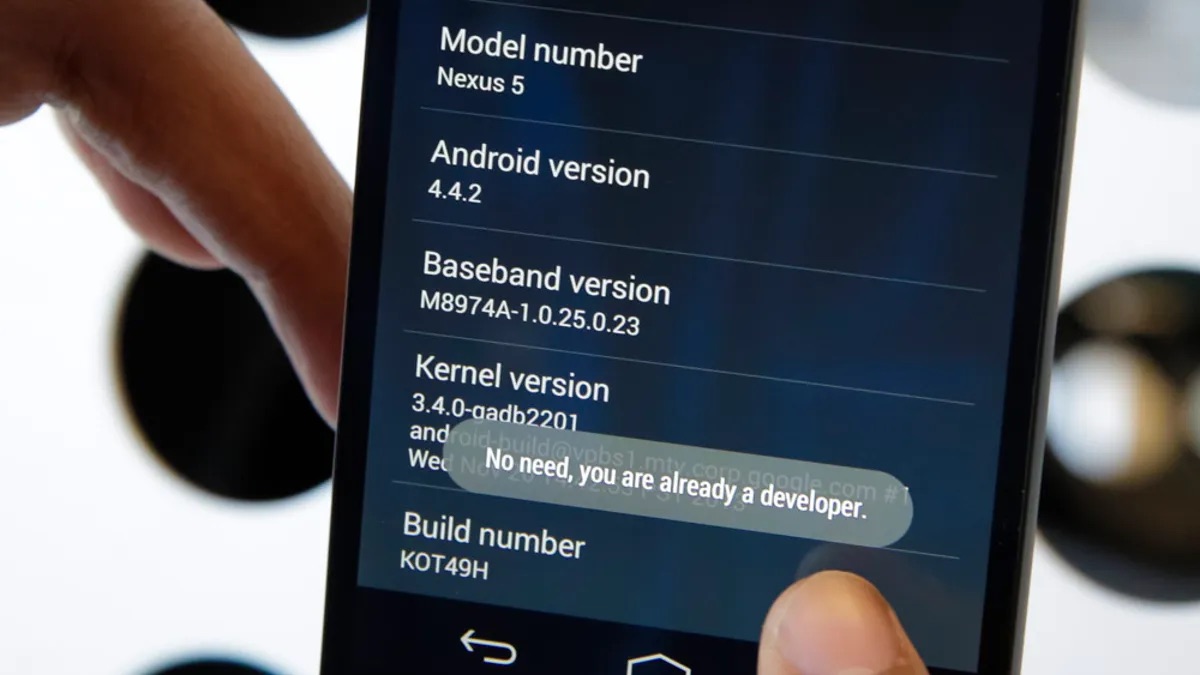
Are you curious if your phone is rooted or not? Rooting your phone gives you access to the deeper levels of your device’s operating system, allowing you to customize and optimize it to your liking. However, not everyone is aware of whether or not their phone has been rooted. In this article, we will delve into the different ways you can tell if your phone has been rooted, helping you gain a better understanding of your device’s capabilities. We will explore both the visible signs and the internal indications that can help you determine if your phone has been rooted, enabling you to take full advantage of its features and functionalities. So, if you’re ready to uncover the truth about your phone’s rooting status, keep reading!
Inside This Article
- Signs that your phone is rooted
- Checking for a rooted phone
- Additional indicators of a rooted phone
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Signs that your phone is rooted
Rooting a phone can provide users with a multitude of benefits, such as customization options and access to advanced features. However, it also comes with certain risks and drawbacks. If you suspect that your phone has been rooted without your knowledge, there are a few telltale signs to look out for.
1. Superuser or SuperSU app: One of the most prominent signs of a rooted phone is the presence of a Superuser or SuperSU app. These apps are necessary to manage and control the root access privileges on your device.
2. Custom recovery: Another indicator of a rooted phone is the presence of a custom recovery such as TWRP (Team Win Recovery Project) or ClockworkMod Recovery. These custom recoveries allow users to perform advanced operations like flashing custom ROMs or creating system backups.
3. Unusual app behavior: If you notice that some of your installed apps behave strangely or stop functioning properly, it could be a sign that your phone has been rooted. Rooting can sometimes interfere with app compatibility and stability.
4. Presence of root-only apps: Certain apps are designed specifically for rooted devices and offer functionalities that are not available on non-rooted phones. If you come across apps that require root access to function, it’s a strong indication that your phone has been rooted.
5. Excessive battery drain: Rooting can sometimes lead to increased battery consumption, especially if poorly optimized custom ROMs or mods are installed. If you notice a sudden decrease in your phone’s battery life, it might be worth investigating if your device has been rooted.
6. Performance issues: Rooting your phone can potentially improve performance by allowing users to tweak system settings. However, if your phone starts experiencing frequent lags, freezes, or crashes after rooting, it could be a sign that something went wrong during the rooting process.
7. Changes in system files: When a phone is rooted, it grants the user full access to system files and directories. If you notice any unauthorized modifications or alterations to system files or folders, it’s a clear indication that your phone has been rooted.
It’s important to remember that these signs are not definitive proof of rooting, as some customizations or apps may mimic rooted behavior. If you suspect your phone has been rooted, it’s advisable to seek professional assistance or use trusted root-detection apps to confirm the status of your device.
Checking for a rooted phone
When it comes to checking if your phone is rooted, there are a few telltale signs that can help you determine whether your device has undergone the rooting process. Here are some steps you can take to check for a rooted phone:
- Look for superuser apps: One of the most obvious indicators of a rooted phone is the presence of superuser apps like SuperSU or Magisk. These apps are typically installed during the rooting process to manage root permissions for other apps.
- Check for custom ROMs: Another way to tell if your phone is rooted is by searching for custom ROMs. Rooting often involves flashing a custom ROM onto your device, which replaces the operating system with a customized version. If you find a different interface or unique features, it could indicate that your phone has been rooted.
- Inspect system files: Advanced users can delve into the system files of their phone to determine if it has been rooted. Look for modified system files or files that don’t belong to the original manufacturer’s software. Additionally, the presence of files like su or busybox is a strong indication of root access.
- Use root-specific apps: There are several apps available on the Play Store that can help you check if your phone is rooted. These apps can detect root access and provide you with detailed information about your device’s root status.
- Check with a root checker app: If you’re unsure or want a straightforward way to check for a rooted phone, you can rely on root checker apps. These apps will quickly determine if your phone has undergone the rooting process.
Remember that rooting your phone can void the warranty and may have security implications. Proceed with caution and only root your device if you understand the risks involved and have a valid reason for doing so.
Additional indicators of a rooted phone
Aside from the traditional methods of checking if your phone is rooted, there are a few additional indicators that can help you determine if your device has been rooted. These indicators may not be foolproof, but they can give you a good idea of whether your phone has undergone the rooting process.
1. Custom ROMs and modifications: One of the most common reasons for rooting a phone is to install custom ROMs or modifications. If you notice unusual bootloader screens, different icon styles, or unique themes on your device, it could be a sign that your phone is running a custom ROM or has undergone modifications that require root access.
2. Unusual system behavior: A rooted phone may exhibit unusual system behavior that is not typically found on a non-rooted device. This can include random reboots, abnormal battery drain, or apps that crash frequently. While these issues can also occur on non-rooted phones, they are more commonly associated with rooted devices due to the system-level changes made during the rooting process.
3. Availability of root-only apps: Rooting a phone allows access to a whole new range of apps that require root permissions. These apps often provide advanced functionality and customization options that are not available on non-rooted devices. If you notice root-only apps installed on your phone or find that you can run apps that require root access, it is a strong indication that your device has been rooted.
4. Superuser or SuperSU app: Many root methods utilize apps like Superuser or SuperSU to manage and control root access. If you find these applications installed on your device, it is a clear indication that your phone has been rooted. These apps typically prompt for permission whenever an app requires root access, allowing you to grant or deny access on a per-app basis.
5. Removal of manufacturer limitations: Rooting a phone often involves bypassing or removing certain limitations imposed by the manufacturer or carrier. If you find that you have access to features or settings that are not available on non-rooted devices, such as the ability to uninstall system apps or tweak system settings, it is a sign that your phone has been rooted.
While these additional indicators can provide valuable insights into whether your phone has been rooted, it’s important to note that they are not definitive proof. Some indicators, like custom ROMs and root-only apps, can be mimicked on non-rooted devices to some extent. If you are unsure about the rooting status of your phone, it’s best to seek professional assistance or use root-checking apps for a more accurate confirmation.
In conclusion, being able to determine whether you have rooted your phone is essential for understanding the capabilities and limitations of your device. Rooting can provide you with greater control over your phone, allowing you to customize it to your liking and access advanced features. However, it also comes with potential risks and voids your warranty. By following the methods mentioned in this article, such as checking for the presence of root-only apps, using root-checking apps, and verifying system file modifications, you can easily ascertain whether your phone has been rooted or not.
Remember, rooting your phone should be done with caution and knowledge, as it can have both positive and negative consequences. Always research and understand the implications before proceeding with such modifications. If you are unsure or uncomfortable with rooting, it is best to seek assistance from a professional or stick to the default settings provided by the manufacturer. With the right information and approach, you can make informed decisions about your phone and enjoy a customized experience that suits your preferences.
FAQs
1. What does it mean to root a phone?
Rooting a phone refers to the process of gaining unrestricted access to the device’s operating system. By doing so, users can bypass limitations imposed by the manufacturer and carrier, which enables them to customize the device, install unauthorized apps, and even modify system settings.
2. How can I tell if my phone is rooted?
There are a few signs to indicate if your phone has been rooted. Firstly, you may notice the presence of unfamiliar apps or system files that you did not install yourself. Additionally, certain apps and functions that require root access, such as Titanium Backup or Xposed Framework, will work on a rooted device but not on an unrooted one. Lastly, you can use root checker apps available on Google Play Store to verify if your phone has been rooted.
3. Is rooting my phone legal?
Rooting a phone itself is not illegal, as it is a process that gives users more control over their device. However, it is worth noting that rooting your phone could potentially void its warranty, as it involves modifying the system files and could lead to security risks if not done properly.
4. Can I unroot my phone?
Yes, it is possible to unroot your phone. There are various ways to do this, depending on the method used to root your device. Some root management apps offer an option to unroot, while others may require manual intervention using a computer and specific software. It is important to follow the unrooting instructions carefully to avoid damaging your phone or losing any important data.
5. What are the benefits of rooting a phone?
Rooting a phone opens up a whole new world of possibilities. Some of the benefits include the ability to install custom ROMs or modified versions of Android, which can enhance performance, provide unique features, and remove manufacturer-installed bloatware. Additionally, users can have full control over system settings, experience improved battery life, and enjoy advanced customization options that are not available on unrooted devices.
