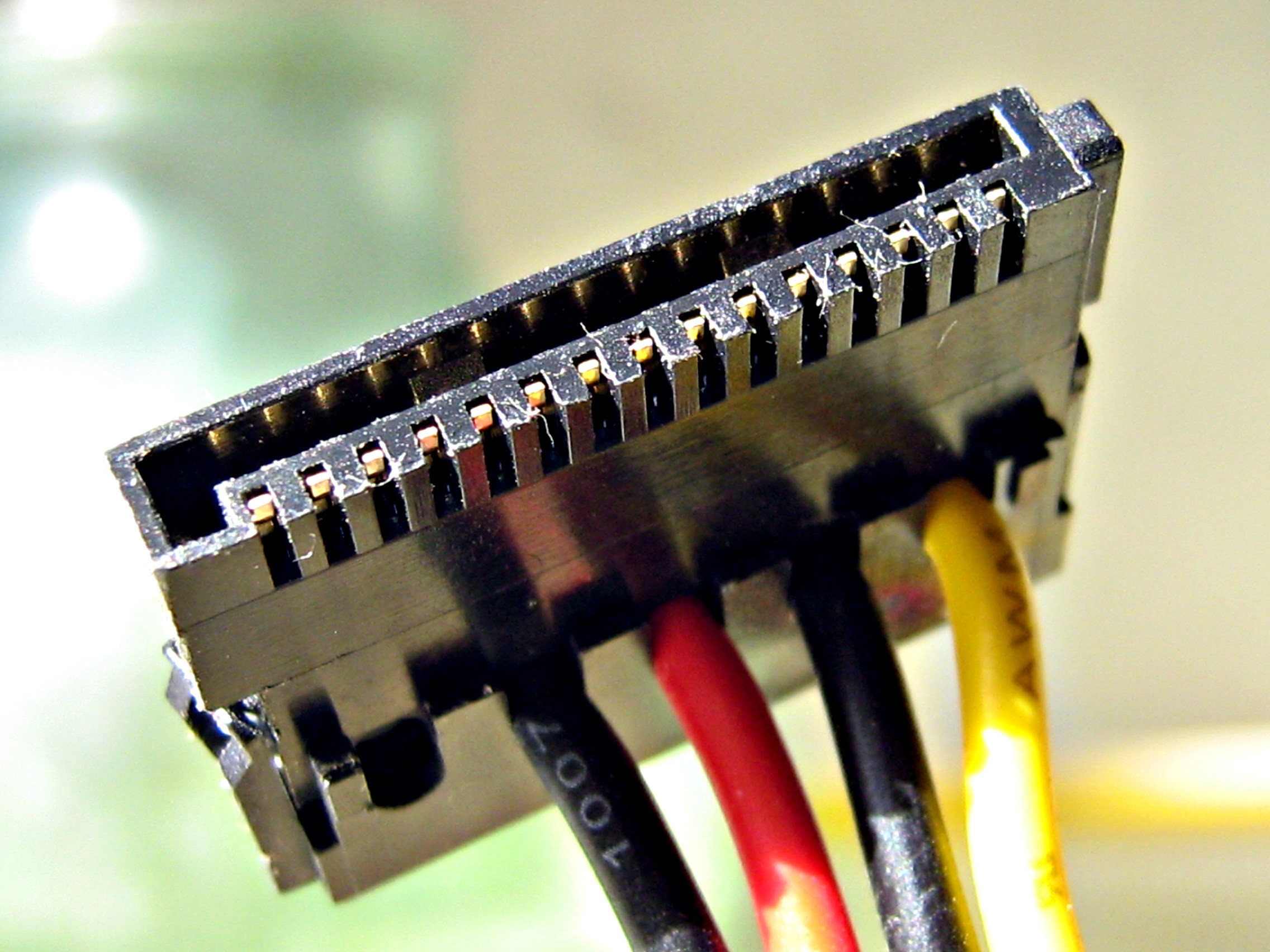
When it comes to understanding the inner workings of a computer, one important component that plays a crucial role is the motherboard. The motherboard is like the central nervous system of a computer, connecting all the different parts and allowing them to communicate with each other. One key aspect of the motherboard is the power connector, which is responsible for supplying the necessary power to the various components of the computer. The power connector on a motherboard is typically in the form of pins, which connect to the power supply to ensure a steady flow of electricity. But how many pins does a motherboard power connector have? In this article, we will explore the different types of motherboard power connectors and discuss the number of pins commonly found in them, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of this essential component of your computer system.
Inside This Article
- The Power Connector on a Motherboard: A Brief Overview
- Understanding the Number of Pins on a Motherboard Power Connector
- Common Types of Motherboard Power Connectors and Their Pin Configurations
- Significance of the Number of Pins on a Motherboard Power Connector
- Conclusion
- FAQs
The Power Connector on a Motherboard: A Brief Overview
When it comes to the power supply of a computer, the motherboard plays a crucial role. It acts as the central hub, connecting all the components and ensuring they receive the power they need to function properly. One of the key components of the motherboard is the power connector. This connector is responsible for delivering power from the power supply unit (PSU) to the motherboard, allowing it to distribute power to other components such as the CPU, RAM, and peripherals.
The power connector on a motherboard typically consists of two parts: the main power connector and the auxiliary power connector. These connectors vary in terms of their pin configurations, which determine the amount of power that can be supplied to the motherboard and its components. It is essential to understand the number of pins on a motherboard power connector to ensure compatibility with the power supply unit.
The number of pins on a motherboard power connector can vary depending on the type and model of the motherboard. The most common types of power connectors found on motherboards are the 20-pin and 24-pin connectors. The 20-pin connector was commonly used in older motherboards, while the 24-pin connector is more commonly found in modern motherboards.
The 20-pin power connector consists of 20 pins arranged in two rows of 10 pins each. It provides power to the core components of the motherboard and is capable of supplying up to 150 watts of power. However, with advancements in technology and the need for more power-hungry components, the 20-pin connector has been largely replaced by the 24-pin connector.
On the other hand, the 24-pin power connector consists of 24 pins arranged in two rows of 12 pins each. It offers a higher power delivery capacity, capable of supplying up to 288 watts of power. This makes it suitable for supporting more demanding components such as high-performance CPUs and graphics cards.
Aside from the main power connectors, some motherboards also feature an auxiliary power connector. This connector provides additional power to specific components, such as the CPU or PCIe slots, ensuring stable operation and preventing power-related issues. The number of pins on the auxiliary power connector can vary, with common configurations being 4-pin, 8-pin, or 4+4 pin connectors.
Understanding the Number of Pins on a Motherboard Power Connector
When it comes to building or upgrading a computer, understanding the various components is essential. One crucial component is the motherboard power connector. This connector is responsible for providing the power necessary to run the motherboard and its associated components. To ensure proper power delivery, motherboards are equipped with power connectors that have a specific number of pins.
Each motherboard power connector is designed to match the power requirements of the motherboard and the components connected to it. The number of pins on a motherboard power connector varies depending on the specific motherboard model and the power needs of the system.
The pins on a motherboard power connector serve different purposes. Some pins are dedicated to providing the necessary voltage to the motherboard, while others are responsible for delivering power to additional components such as the CPU, GPU, and storage devices.
The number of pins on a motherboard power connector directly affects the power delivery capabilities of the motherboard. A higher number of pins allows for a greater power capacity, ensuring that all components receive an adequate and stable power supply. Conversely, a lower number of pins may limit the power delivery capacity and restrict the performance of power-hungry components.
It’s important to note that different types of motherboards come with different power connector configurations. The most commonly used motherboard power connectors are the 20-pin ATX connector, the 24-pin ATX connector, and the 8-pin EPS connector.
The 20-pin ATX connector was commonly used in older motherboards, but it is now less commonly found in newer systems. The 24-pin ATX connector has become the standard for modern motherboards, offering improved power delivery and compatibility with a wider range of components.
The 8-pin EPS connector is specifically designed to provide additional power to power-hungry components, such as high-end CPUs. It ensures stable power delivery to support demanding workloads and overclocking capabilities.
Common Types of Motherboard Power Connectors and Their Pin Configurations
When it comes to powering a motherboard, there are several different types of power connectors that may be used. Each type has its own unique pin configuration, which determines how power is supplied to the motherboard. Understanding these power connectors and their pin configurations is essential for proper installation and compatibility. Let’s take a closer look at the most common types of motherboard power connectors:
1. ATX 24-Pin Power Connector:
The ATX 24-pin power connector is one of the most common power connectors found on modern motherboards. As the name suggests, it consists of 24 pins arranged in a specific configuration. This power connector provides the primary power supply to the motherboard, delivering power to the CPU, RAM, and other critical components.
2. EPS 8/4-Pin Power Connector:
The EPS 8/4-pin power connector is designed specifically for supplying power to the CPU. It consists of either 8 or 4 pins, depending on the motherboard’s requirements. This connector ensures stable and reliable power delivery to the CPU, making it crucial for proper system performance.
3. PCIe 6/8-Pin Power Connector:
The PCIe 6/8-pin power connector is used to provide additional power to the graphics card. It is commonly found on high-performance motherboards and is crucial for powering graphics cards that require extra power beyond what the PCIe slot can provide. The connector can accommodate either 6 or 8 pins, depending on the graphics card’s power requirements.
The SATA power connector is primarily used to supply power to storage devices, such as hard drives and SSDs. It features a distinctive L-shaped design and is commonly found on motherboards supporting SATA interfaces. This connector provides a stable power supply to ensure the proper functioning of storage devices.
5. Molex Power Connector:
The Molex power connector, also known as the Peripheral power connector, is an older power connector found on some motherboards. It is typically used to power peripherals such as fans, optical drives, and older hard drives. The Molex connector consists of four pins arranged in a square configuration.
6. 4-Pin PWM Fan Connector:
The 4-pin PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) fan connector is used to supply power to the CPU cooling fan or case fans. It allows for more precise control over fan speeds, resulting in quieter operation and better thermal management. This connector is often found near the CPU socket on the motherboard.
7. USB Header:
While not strictly a power connector, the USB header on a motherboard is worth mentioning. It allows for additional USB ports to be connected directly to the motherboard, providing both power and data connectivity. This is particularly useful for expanding the number of external devices that can be connected to the system.
It’s important to note that the specific types and pin configurations of power connectors can vary depending on the motherboard model and manufacturer. It’s always recommended to consult the motherboard’s manual or specifications to identify the exact power connectors and their pin configurations before installation.
Significance of the Number of Pins on a Motherboard Power Connector
When it comes to a motherboard’s power connector, the number of pins plays a crucial role in determining its capabilities and compatibility. The pin configuration of the power connector determines the amount of electrical power that can be supplied to the motherboard and its components.
Each pin on the power connector is responsible for carrying a specific type of electrical signal or power supply. The number and arrangement of pins vary depending on the type of power connector used. Understanding the significance of the number of pins will help you choose the right power supply for your motherboard and ensure optimal performance.
The number of pins on a motherboard power connector directly corresponds to the power requirements and capabilities of the motherboard. Generally, a higher number of pins indicates a larger power capacity. With more pins, the power connector is capable of delivering higher currents and voltages to meet the demands of power-hungry components like processors and graphics cards.
For example, the most commonly used power connector for motherboards is the ATX power connector, which typically has either a 20-pin or a 24-pin configuration. The 24-pin configuration provides higher power capacity compared to the 20-pin configuration. This difference allows the motherboard to receive more stable power and support power-hungry components without straining the power supply.
Another critical aspect to consider is backward compatibility. Motherboard power connectors are often designed to be backward compatible, meaning that a connector with more pins can also work with motherboards that require a lower number of pins. For instance, a 24-pin power connector can be used with a motherboard that has a 20-pin power input, but not vice versa.
It is worth noting that the power connector on a motherboard is not compatible with every power supply. Different types of motherboards require different types of power connectors with specific pin configurations. Therefore, it is essential to ensure compatibility between the motherboard and the power supply to avoid any compatibility issues.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the number of pins on a motherboard power connector is essential for any tech enthusiast or computer builder. The power connector is crucial for delivering the necessary power to your motherboard and ensuring a stable and reliable computer system. By knowing the number of pins, you can ensure compatibility between the power supply unit and motherboard.
Typically, motherboards have either 20 or 24-pin connectors, with the latter being more common for modern computers. It is important to choose a power supply unit that matches the motherboard’s power connector to ensure that all components receive the appropriate power supply.
If you are unsure about the number of pins on your motherboard power connector, consult the manufacturer’s specifications or user manual. Additionally, there are online resources and forums where you can find detailed information about specific motherboard models.
Overall, having the correct number of pins on your motherboard power connector is crucial for the proper functioning and stability of your computer system. Make sure to double-check compatibility to avoid any potential issues and enjoy a smooth computing experience.
FAQs
1. How many pins does a motherboard power connector have?
The majority of modern motherboards typically have a 24-pin power connector. This connector is responsible for providing power to various components on the motherboard, such as the CPU, memory, and expansion slots.
2. Can I use a different power supply with a motherboard that has a different pin configuration?
No, it is important to match the pin configuration of the power supply with the motherboard’s power connector. Using a power supply with a different pin configuration can lead to compatibility issues and even damage the motherboard and other components.
3. Are there any additional power connectors required for high-end motherboards?
Yes, high-end motherboards often require additional power connectors to provide the necessary power for overclocking and other demanding tasks. These additional connectors, such as 8-pin or 4+4-pin CPU power connectors, are usually located near the CPU socket.
4. What happens if I don’t connect all the necessary power connectors?
If you fail to connect all the necessary power connectors, your computer may not power on or may experience stability issues. Certain components, such as the CPU and GPU, require sufficient power to operate correctly, and without the proper connections, these components may not function properly.
5. Can I use adapters or converters for incompatible power connectors?
While there are adapters and converters available to convert power connectors, it is generally not recommended to use them. These adapters may not provide the necessary power or stability required by the motherboard and its components. It’s best to choose a power supply that matches the motherboard’s power connector to ensure compatibility and proper functionality.
