Tableau is a powerful data visualization tool that allows users to create interactive and insightful visualizations. One common challenge that Tableau users encounter is the need to replace the data source used in their visualizations. This can occur when the original data source is updated, or when there is a need to switch to a different data set.
Replacing the data source in Tableau is a crucial skill to master, as it ensures that your visualizations continue to reflect the most up-to-date and accurate information. In this article, we will guide you through the process of replacing the data source in Tableau, providing you with step-by-step instructions and insights to help you seamlessly transition to a new data set. So, whether you’re a beginner or an experienced Tableau user, let’s dive in and master the art of replacing data sources in Tableau!
Inside This Article
- Overview
- Understanding Data Sources in Tableau
- Steps to Replace a Data Source in Tableau
- Best Practices for Replacing Data Sources in Tableau
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Overview
Are you struggling with outdated or inaccurate data in your Tableau dashboard? Don’t worry! This article will guide you through the process of replacing a data source in Tableau, ensuring that your visualizations are always based on the most up-to-date and reliable information.
Tableau is a powerful data visualization tool that allows users to connect and analyze data from various sources. However, there are instances where the original data source may need to be changed due to data updates, changes in the data structure, or simply the need to use a different dataset. The process of replacing a data source in Tableau ensures that your dashboards remain dynamic and can adapt to the changing data landscape.
In this article, we will explore the concept of data sources in Tableau, understand why replacing them is necessary, and provide you with step-by-step instructions on how to replace a data source effectively. Additionally, we will share some best practices to ensure a smooth transition and maintain the integrity of your visualizations.
Understanding Data Sources in Tableau
Data sources play a crucial role in Tableau, as they are the foundation of any analysis or visualization. In Tableau, a data source is a file, database, or connection that contains the data you want to explore and analyze. It provides the raw data that Tableau uses to create visualizations and generate insights. Understanding data sources in Tableau is essential for effectively using the platform and getting the most out of your data.
Tableau supports a wide range of data sources, including Excel spreadsheets, CSV files, databases like MySQL or Oracle, cloud-based data warehouses such as Amazon Redshift, and even web-based data sources like Google Analytics. This flexibility allows you to connect to and analyze data from various sources, helping you gain a holistic view of your business or project.
One of the key advantages of Tableau is its ability to handle large and diverse data sets. Whether you have millions of rows of transactional data or a small dataset with just a few columns, Tableau can efficiently handle and visualize the data. By understanding the characteristics of your data source, such as the data types, relationships, and structure, you can effectively manipulate and analyze the data to generate meaningful insights.
Tableau also allows you to blend multiple data sources together. This feature is particularly beneficial when you have data spread across multiple systems or databases. By combining data from different sources, you can identify correlations, uncover hidden trends, and gain deeper insights into your data.
Moreover, Tableau provides options for data extraction and data connection. Data extraction imports a subset of the data into Tableau’s proprietary format, which enhances performance and allows for offline analysis. On the other hand, data connection establishes a live connection to the data source, enabling real-time analysis and automatic updates as the underlying data changes.
Understanding the capabilities and limitations of your data source in Tableau is important. For example, some sources may have limits on the number of rows or columns that can be accessed, while others may have restrictions on the type of data manipulation that can be performed. By being aware of these considerations, you can make informed decisions about how to structure your analysis and maximize the value of your data.
Steps to Replace a Data Source in Tableau
Replacing a data source in Tableau is a straightforward process that allows you to seamlessly switch between different data sets while maintaining your existing visualizations. This can be useful when you need to update your analysis with new data or when you want to use a different data source for comparison.
Here are the steps to replace a data source in Tableau:
- Open your workbook: Launch Tableau and open the workbook that contains the existing data source you want to replace.
- Go to the Data Source tab: Once the workbook is open, navigate to the Data Source tab at the bottom of the screen. This is where you can view and manage the data sources used in your workbook.
- Select the data source: In the Data Source tab, identify the data source you want to replace. It will be listed under the “Connections” section.
- Right-click on the data source: Right-click on the data source you want to replace to open a drop-down menu of options.
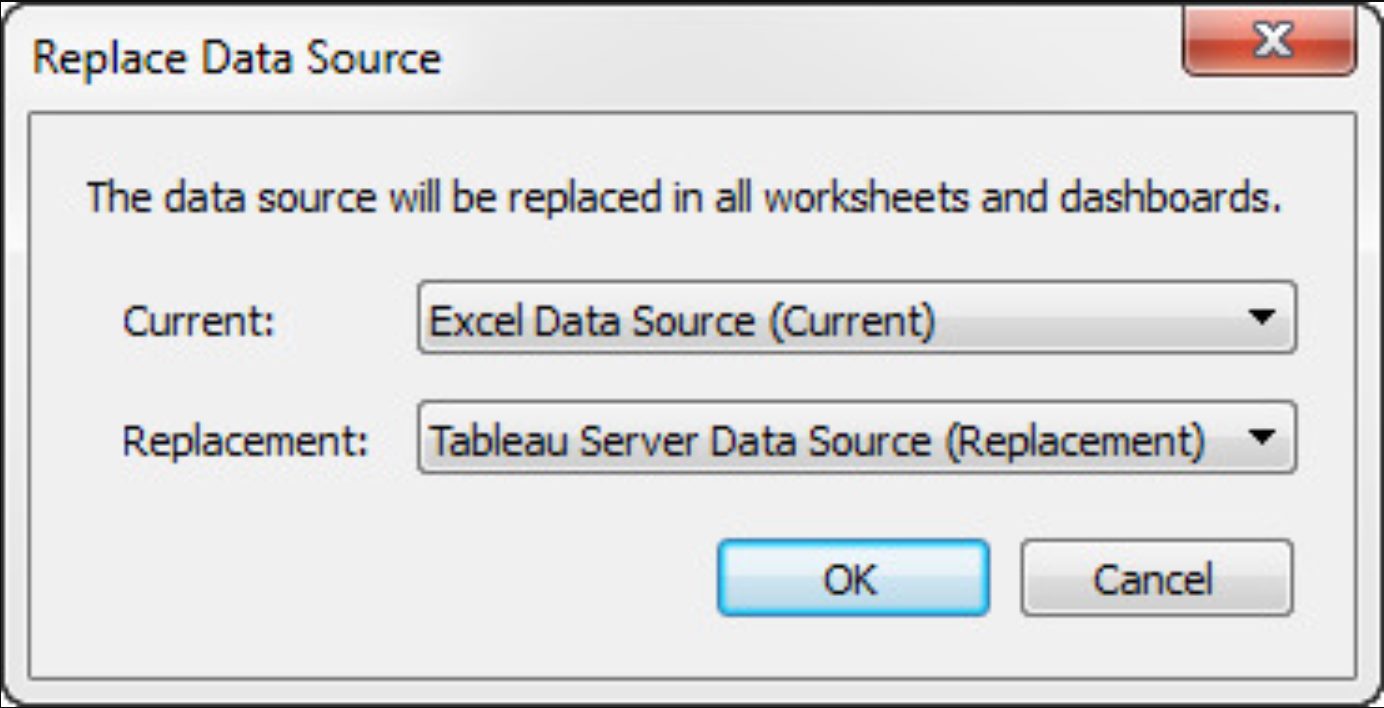
- Choose “Replace Data Source”: From the drop-down menu, select the option that says “Replace Data Source.” This will open a dialog box where you can browse for the new data source.
- Browse and select the new data source: In the dialog box, navigate to the location of the new data source file on your computer. Select the file and click “Open” to replace the existing data source.
- Map the fields: Once the new data source is selected, Tableau will automatically map the fields between the old and new data sources based on their names and data types. However, it’s important to review the field mappings and make any necessary adjustments to ensure accurate data analysis.
- Refresh your workbook: After mapping the fields, click “OK” in the dialog box to replace the data source. Tableau will refresh your workbook to update all the visualizations and calculations based on the new data source.
By following these steps, you can easily replace a data source in Tableau and continue your analysis with the updated or alternative data. It is important to note that the process may vary slightly depending on the version of Tableau you are using, but the overall concept remains the same.
Best Practices for Replacing Data Sources in Tableau
When it comes to replacing data sources in Tableau, following a set of best practices can help ensure a smooth and efficient transition. Whether you’re updating your data, switching to a different database, or migrating to a new server, these tips will help you navigate the process effectively.
1. Understand your data structure: Before replacing a data source, take the time to thoroughly understand the structure of your existing data. Familiarize yourself with the fields, calculations, and relationships within the dataset. This will help you identify any potential challenges or changes needed when replacing the data source.
2. Check for compatibility: When replacing a data source, it’s crucial to ensure compatibility between the old and new sources. Verify that the fields, data types, and formatting match to prevent any data discrepancies or errors. Additionally, consider any specific requirements or limitations associated with the new data source.
3. Test and validate: Before fully replacing a data source, test the new source with a subset of data to ensure everything is functioning as expected. Validate that calculations, filters, and visualizations are producing accurate results. By conducting thorough testing, you can identify and address any issues before implementing the replacement.
4. Save your work: Always make a backup of your workbook or data source before performing any replacements. This precautionary measure ensures that you have a safe copy to revert to in case anything goes wrong during the process. Saving a backup will save you valuable time and effort in the event of any unexpected issues.
5. Communicate with stakeholders: If you are replacing a data source that is shared with other users or departments, it is important to communicate the changes in advance. Informing stakeholders about the replacement and any potential impact on their analysis or workflows will minimize surprises and allow for a smooth transition.
6. Update data connections: Once you have successfully replaced your data source, remember to update any data connections within your Tableau workbook. This includes refreshing extracts, re-establishing live connections, or modifying connection details as necessary. Ensuring that your workbook is connected to the updated data source will avoid any disruptions in your analysis.
7. Document the changes: It’s essential to document the changes you made while replacing the data source. Keep track of the steps you took, any modifications you made, and any issues encountered along the way. This documentation will serve as a valuable reference for future updates or troubleshooting. It’s also helpful for collaborating with team members and sharing knowledge within your organization.
By following these best practices, you’ll be well-equipped to replace data sources in Tableau with confidence and efficiency. With a solid understanding of your data structure, compatibility checks, thorough testing, backups, clear communication, updated connections, and detailed documentation, you’ll ensure a seamless transition and maintain the integrity of your analysis workflow.
Conclusion
Replacing a data source in Tableau is an essential skill that every Tableau user should have. Whether you need to update the data connection to a different file, a new database, or a refreshed data set, understanding the process of replacing the data source can save you time and effort.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can seamlessly switch your data source in Tableau without losing any of your existing visualizations, calculations, or filters. Remember to double-check the field mappings, data types, and join conditions when replacing your data source to ensure accurate analysis and reporting.
With the ability to easily swap out data sources, Tableau empowers you to explore and analyze data from different perspectives, drive data-driven insights, and make more informed decisions. So go ahead and confidently replace your data source in Tableau, knowing that you can effortlessly adapt and work with the data you need.
FAQs
FAQ 1: How do I replace the data source in Tableau?
FAQ 2: What happens to my visualizations and calculations when I change the data source in Tableau?
FAQ 3: Can I replace a data source with a different file type in Tableau?
FAQ 4: Is it possible to replace a data source with a live connection to a database in Tableau?
FAQ 5: Will replacing the data source affect the filters and parameters set in my Tableau workbook?
