Are you in the process of building your own computer or troubleshooting an issue with your current setup? If so, you may have come across the term “SATA connector” and wondered where exactly it is located on your motherboard. The SATA connector plays a vital role in connecting your hard drives, solid-state drives, and other storage devices to your computer system.
In this article, we will explore the location of the SATA connector on a motherboard and provide you with valuable insights on how to identify and utilize it effectively. Whether you are a novice or an experienced computer enthusiast, understanding the SATA connector and its placement on the motherboard can make a significant difference in optimizing your computer’s storage capabilities.
Inside This Article
- Why SATA Connectors are Important
- Different Types of SATA Connectors
- Locating the SATA Connector on the Motherboard
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Why SATA Connectors are Important
SATA connectors are an essential component when it comes to connecting various devices to a motherboard. These small yet mighty connectors play a crucial role in the functionality and performance of your computer system. Let’s explore why SATA connectors are so important:
1. Data Transfer Speed: One of the primary reasons SATA connectors are vital is their ability to provide high-speed data transfer. With SATA connectors, you can enjoy faster data transmission rates, allowing for quicker file transfers, improved system responsiveness, and efficient operation of your storage devices.
2. Compatibility: SATA connectors are widely compatible with a range of devices, making them a versatile choice for connecting different components to your motherboard. Whether you’re connecting a hard drive, solid-state drive (SSD), optical drive, or even an external storage device, SATA connectors ensure seamless compatibility and connectivity.
3. Power Delivery: In addition to data transfer, SATA connectors also serve as a power delivery mechanism. They provide power to your connected storage devices, eliminating the need for separate power cables and simplifying the overall system setup. This streamlined power delivery enhances efficiency and reduces clutter within your computer case.
4. Hot Swapping: SATA connectors allow for hot swapping, enabling you to connect or disconnect storage devices while your computer is still running. This feature is particularly useful for external storage devices or for replacing faulty hard drives without shutting down your system. It offers convenience and flexibility without disrupting your workflow.
5. Expansion Options: With multiple SATA connectors available on most motherboards, you have the flexibility to expand your storage capacity easily. You can connect additional hard drives or SSDs to handle growing data demands, whether it’s for gaming, multimedia editing, or large file storage. SATA connectors make it convenient to scale your storage as needed.
Different Types of SATA Connectors
SATA connectors are essential components that allow you to connect various devices to your motherboard, such as hard drives and solid-state drives (SSDs). They provide a reliable and high-speed data transfer interface, ensuring seamless communication between your motherboard and storage devices.
There are different types of SATA connectors, each designed for specific purposes and requirements. Let’s explore the most common types:
- SATA 1.0: This is the original SATA standard, offering a maximum data transfer rate of 1.5 gigabits per second (Gbps). While it may be slower compared to newer versions, it is still widely supported by older systems.
- SATA 2.0: Also known as SATA II, this version provides a higher data transfer rate of 3 Gbps. It is backward compatible with SATA 1.0, allowing you to use SATA II drives with older motherboards.
- SATA 3.0: Referred to as SATA III, this is the most common SATA standard found in modern motherboards. It offers a blazing-fast data transfer rate of 6 Gbps, allowing for faster performance and improved system responsiveness.
- eSATA: Standing for external SATA, eSATA connectors are designed specifically for connecting external storage devices. They provide the same data transfer rate as the corresponding internal SATA standard (e.g., eSATA III offers 6 Gbps), but in an external format.
- mSATA: Unlike the traditional SATA connectors, mSATA connectors are smaller and designed for use with smaller devices like laptops or compact motherboards. They provide a space-saving solution while still delivering reliable performance.
- M.2: M.2 connectors have gained popularity in recent years due to their compact form factor and high data transfer speeds. They are commonly used for connecting SSDs and wireless modules, offering speeds of up to 32 Gbps in some cases.
It is important to note that compatibility between SATA connector types is crucial. For example, a SATA III drive can be used with a SATA II connector, but it will only operate at SATA II speeds. Similarly, a SATA II drive connected to a SATA III connector will still function, but the transfer rate will be limited to SATA II capabilities.
Understanding the different types of SATA connectors enables you to choose the right hardware for your system and ensure optimal performance. Whether you’re building a new computer or upgrading an existing one, it’s essential to consider the SATA connector compatibility with your motherboard and storage devices to make the most out of your system’s capabilities.
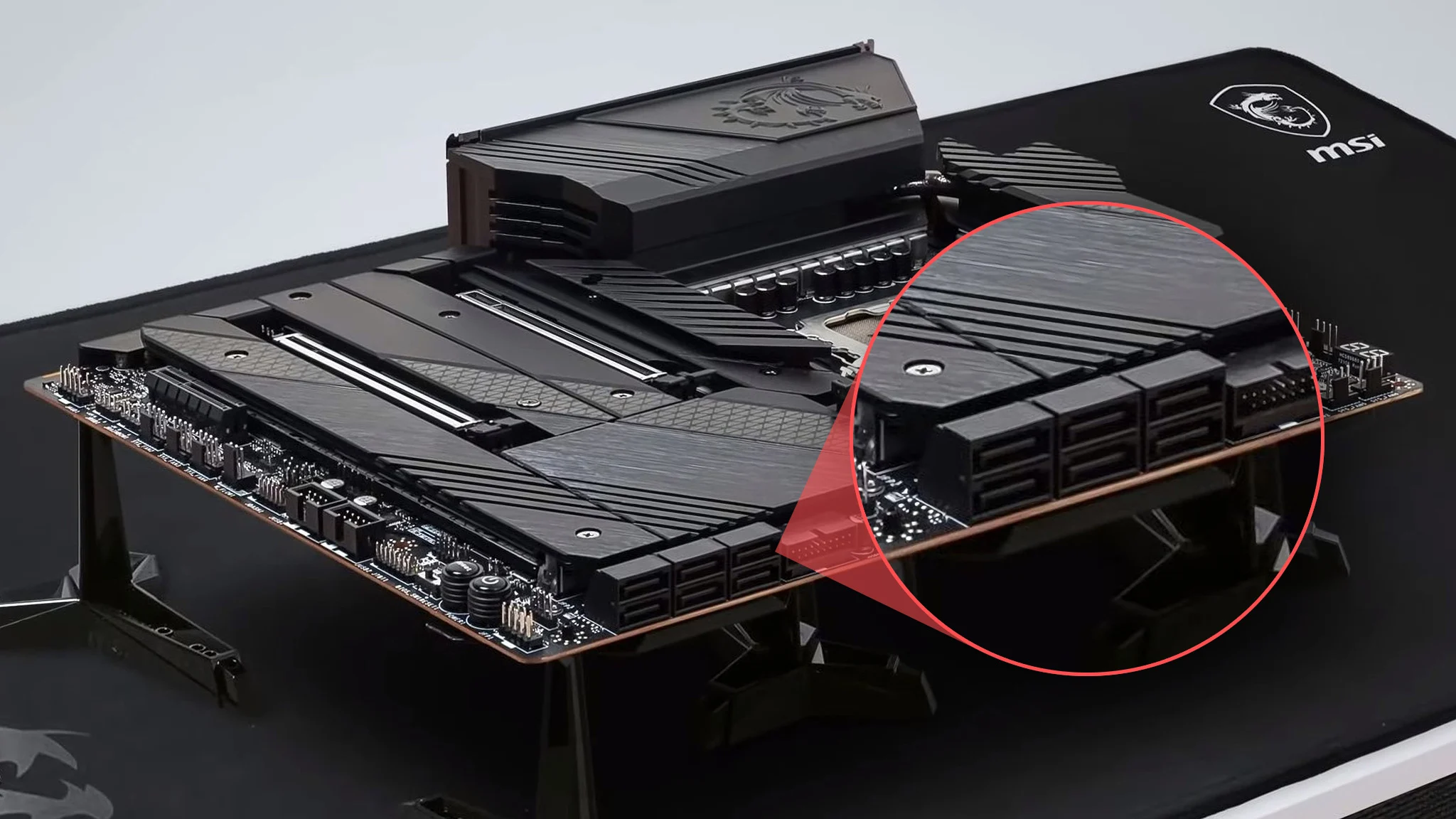
Locating the SATA Connector on the Motherboard
When it comes to connecting storage devices to your computer, the SATA connector plays a crucial role. Whether you want to install a solid-state drive (SSD), a traditional hard drive (HDD), or an optical drive, the SATA connector is what allows for a high-speed and reliable connection. But where exactly can you find the SATA connector on your motherboard?
Typically, the SATA connectors on a motherboard are located near the edge of the board, closer to the storage bays or slots. The exact placement can vary depending on the motherboard manufacturer and model, but you can easily locate it with a bit of visual inspection.
If you take a close look at your motherboard, you will notice a series of small rectangular or L-shaped connectors. These are the SATA connectors. They are usually color-coded, with the most common colors being black, white, or blue. The number of SATA connectors can also vary depending on the motherboard, but most modern motherboards provide multiple SATA ports to cater to different storage needs.
Another way to identify the SATA connectors is by referring to the motherboard’s manual or documentation. The manual will provide detailed information about the layout and placement of all the connectors on the motherboard, including the SATA connectors. It’s a good idea to keep the motherboard manual handy as a reference whenever you need to connect or disconnect any storage devices.
Once you have located the SATA connectors on your motherboard, you are ready to connect your storage devices. The SATA connectors consist of two main components: the data connector and the power connector. The data connector is a small L-shaped connector that uses a thin cable to transmit data between the motherboard and the storage device. The power connector, on the other hand, provides power to the storage device through a separate cable.
It’s important to note that SATA connectors are designed to be hot-swappable, which means you can connect or disconnect storage devices while the computer is powered on. However, it is always recommended to shut down your computer before making any hardware changes to avoid any potential risks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the location of the SATA connector on a motherboard is crucial for anyone looking to add or upgrade storage devices in their computer. The SATA connector is typically found near the edge of the motherboard, close to the SATA ports on the back panel. It is important to consult the motherboard manual or utilize online resources to precisely locate the SATA connector, as its position can vary depending on the motherboard model.
By familiarizing yourself with the layout of the motherboard and identifying the SATA connector, you can easily connect and manage storage devices, such as hard drives, solid-state drives, and optical drives, to enhance the functionality of your computer.
Whether you are a tech enthusiast building a custom PC or an individual looking to expand storage capacity, knowing the location of the SATA connector on your motherboard will save you time and frustration during the installation process. So, take the time to explore your motherboard and find that pivotal SATA connector – it can make all the difference in creating an efficient and powerful computer setup.
FAQs
1. Where is the SATA connector located on a motherboard?
The SATA connectors on a motherboard are typically located along the edge of the board or in close proximity to the storage ports. These connectors are often grouped together in clusters and can be found near the ATX power supply connector. However, it’s essential to refer to the specific motherboard’s user manual or diagram for the exact location as it may vary depending on the motherboard model and manufacturer.
2. How does a SATA connector look like?
A SATA connector is a small rectangular-shaped port typically featuring an L-shaped design. It consists of seven pins or more, depending on the SATA revision, arranged in a specific pattern. The connector has a plastic housing with a latch mechanism or a clip on one side to secure the SATA cable once plugged in.
3. Can I connect multiple devices to a single SATA connector?
No, a single SATA connector supports only one device connection. Each SATA port on the motherboard is designed to accommodate a single SATA cable, which can be connected to a storage device such as a solid-state drive (SSD) or a hard disk drive (HDD). If you need to connect multiple devices, you will require additional SATA connectors or the usage of SATA port multipliers.
4. What is the purpose of a SATA connector?
The SATA connector enables the communication between the motherboard and various storage devices such as SSDs, HDDs, and optical drives. It transmits data and provides power to these devices, allowing them to function properly. The SATA interface has become the standard for modern storage devices due to its faster data transfer rates and improved reliability compared to its predecessor, the IDE interface.
5. Can I use a different connector instead of SATA?
While SATA is the most common and widely used connector for storage devices, there are alternative connectors available depending on the device and motherboard compatibility. For example, M.2 and PCIe connectors are used for high-performance SSDs, while older systems may still have IDE connectors. It’s important to check the compatibility of your storage device and motherboard before attempting to use a different connector.
