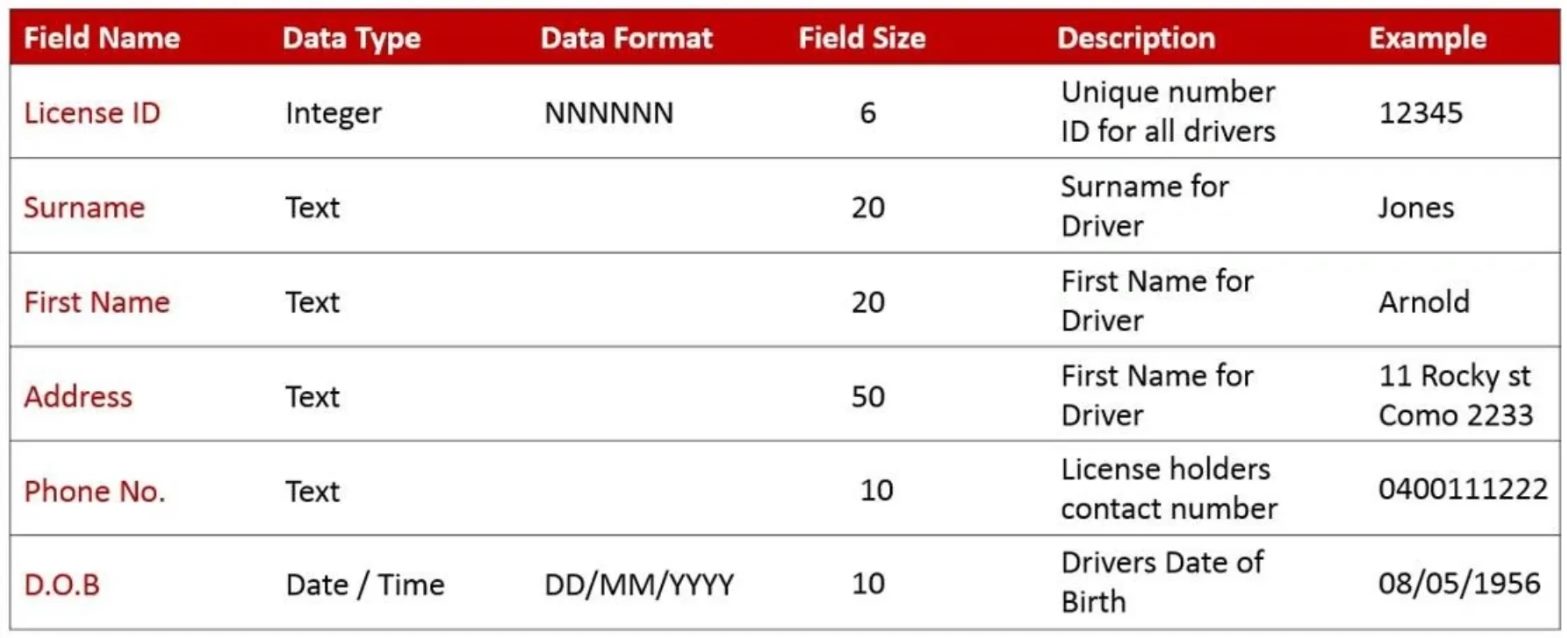
Are you tired of struggling to understand and manage your data? Do you find yourself wasting time searching for important information within your datasets? If so, it’s time to create a data dictionary! A data dictionary is a powerful tool that helps you organize, document, and make sense of your data. In this article, we will guide you through the process of creating a data dictionary, step by step, so you can take control of your data and improve the efficiency and effectiveness of your data management efforts. Whether you are a data analyst, a database administrator, or simply someone who wants to better understand their data, this article will provide you with the knowledge and techniques you need to create a comprehensive and useful data dictionary. So let’s dive in and make your data management tasks a breeze!
Inside This Article
- Purpose of a Data Dictionary
- Key Components of a Data Dictionary
- Steps to Create a Data Dictionary
- Best Practices for Maintaining a Data Dictionary
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Purpose of a Data Dictionary
A data dictionary is an essential tool for any organization that deals with data. It serves as a central repository of information about the data elements used in a system or database. The primary purpose of a data dictionary is to provide a detailed description of each data element, including its name, data type, length, format, and the meaning or purpose it serves within the system.
One of the main benefits of a data dictionary is that it promotes data consistency and accuracy. By documenting the structure and characteristics of the data, it ensures that all users and stakeholders have a clear understanding of how the data should be interpreted and used. This helps to avoid confusion, reduce errors, and improve data quality.
Another important purpose of a data dictionary is to enhance data governance and data management practices. It serves as a vital reference for data stewards, data analysts, and database administrators, enabling them to effectively manage and control data assets. With a comprehensive data dictionary in place, organizations can establish standardized processes for data integration, data migration, and data reporting.
In addition to its role in promoting data consistency and governance, a data dictionary also plays a crucial role in facilitating communication and collaboration among teams. It serves as a common language for data-related discussions, allowing individuals from different departments or units to understand and interpret the data in a consistent manner. This promotes effective decision-making and improves collaboration on data-intensive projects.
Overall, the purpose of a data dictionary is to provide a comprehensive and reliable source of information about data elements within an organization. It serves as a valuable resource for data governance, data management, and data analysis, ultimately helping organizations make informed decisions based on accurate and consistent data.
Key Components of a Data Dictionary
A data dictionary plays a crucial role in managing and understanding the information assets within an organization. It serves as a central repository for all metadata related to the data and provides a comprehensive overview of the data elements and their attributes. Let’s delve into the key components that make up a data dictionary:
1. Data Elements: The data elements are the building blocks of a data dictionary. These represent the specific pieces of data that are captured and stored within a system or database. Each data element has a unique name and is accompanied by a description that provides additional context and meaning.
2. Data Attributes: Data attributes provide detailed information about the characteristics or properties of the data elements. They describe the data type, length, format, allowed values, and any constraints or validations that apply to the data element.
3. Relationships: A data dictionary also captures the relationships between different data elements. This includes relationships such as parent-child relationships, dependencies, and associations, which help establish the contextual connections between various data elements.
4. Data Source: The data dictionary should include information about the source of the data. This could be internal or external sources, databases, files, or APIs. Specifying the data source helps ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data recorded in the dictionary.
5. Data Usage: Data usage refers to the intended purpose or usage of the data elements. It provides insights into how the data is used in various processes, reports, or applications within the organization. Understanding data usage helps in making informed decisions regarding data governance and management.
6. Data Documentation: The data dictionary should include clear and concise documentation for each data element. This documentation should explain the purpose, context, and business rules associated with the data. It also helps in maintaining consistency and ensuring proper understanding and interpretation of the data elements.
7. Data Security: Data security is a critical component of a data dictionary. It should outline the access controls, permissions, and restrictions that govern who can view or modify the data elements. This ensures that sensitive or confidential information is protected and accessed only by authorized personnel.
8. Data Governance: Data governance refers to the policies, procedures, and guidelines that govern the management and use of data within an organization. The data dictionary should align with the organization’s data governance framework to ensure compliance and consistency in data management practices.
By incorporating these key components into a data dictionary, organizations can effectively document and manage their data assets, enabling better data understanding, decision-making, and data governance practices.
Steps to Create a Data Dictionary
A data dictionary is an essential tool for managing and understanding the data within a project or organization. It serves as a centralized repository of information about the data, including its structure, attributes, and relationships. To create a data dictionary effectively, follow these steps:
- Identify the Project Scope: Begin by defining the scope of your data dictionary. Determine the specific data sets or systems you want to document and analyze. This will help you focus your efforts and ensure that you capture all the necessary information.
- Collect Data Inventory: Next, gather an inventory of all the data sources and data objects that you plan to include in the data dictionary. This can include databases, spreadsheets, and any other data repositories that are relevant to your project.
- Define Data Elements: For each data object, identify and define the data elements or attributes that need to be documented. These can include fields, columns, tables, or any other units of data that are relevant within the context of your project.
- Document Data Details: Once you have identified the data elements, document the specific details for each one. This can include the data type, length, format, allowed values, and any validation rules or constraints that apply.
- Capture Data Relationships: Identify and document the relationships between different data objects. This can include primary key-foreign key relationships, one-to-many or many-to-many relationships, and any other dependencies or associations that exist.
- Add Descriptive Information: Include additional descriptive information about each data element, such as its purpose, business rules, data sources, and any relevant documentation or references.
- Organize and Structure: Arrange the data dictionary in a logical and intuitive manner. Use headings, sections, and sub-sections to group related information and make it easier to navigate and understand.
- Validate and Review: Once you have created the initial version of the data dictionary, validate and review the information with relevant stakeholders. Ensure that the documentation is accurate, complete, and aligned with the requirements and objectives of the project.
- Maintain and Update: Finally, establish a process for maintaining and updating the data dictionary. As data structures and requirements evolve, it is important to keep the documentation up to date to reflect any changes or additions.
By following these steps, you can create a comprehensive and valuable data dictionary that will serve as a valuable resource for managing and understanding your data assets.
Best Practices for Maintaining a Data Dictionary
Once you have created a data dictionary, it is important to establish proper maintenance practices to ensure its effectiveness and accuracy over time. Here, we will discuss some best practices to help you maintain your data dictionary efficiently.
- Regular Updates: Keep your data dictionary up to date by implementing a schedule for regular updates. As your data evolves, new fields may be added or existing ones may change. By keeping your data dictionary current, you ensure that everyone in your organization has access to the most accurate and relevant information.
- Version Control: Implement a version control system for your data dictionary. This allows you to track changes and revisions to the dictionary, providing a clear history of modifications. Version control ensures that you can easily revert back to a previous version if needed and helps maintain data integrity.
- Collaboration: Encourage collaboration among your team members when maintaining the data dictionary. Establish clear roles and responsibilities for updating and reviewing the dictionary. By involving multiple stakeholders in the maintenance process, you benefit from their expertise and ensure that the dictionary reflects the diverse perspectives within your organization.
- Documentation: Document any changes that are made to the data dictionary. This includes recording the reasons for the changes, the individuals involved, and the date of the modification. Proper documentation provides transparency and accountability, making it easier to track the evolution of the data dictionary and understand the rationale behind specific changes.
- Training and Communication: Provide training to your team members on how to use the data dictionary and emphasize its importance. Clear communication channels should be established to address any questions or concerns regarding the data dictionary. Regularly remind your team about the existence of the data dictionary and encourage its use in all data-related processes.
- Metadata Governance: Establish metadata governance policies and procedures to govern the use and management of the data dictionary. This includes defining guidelines for naming conventions, data standards, and data documentation practices. By setting clear rules and standards, you ensure consistency and accuracy throughout the data dictionary.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of your data dictionary to identify any inconsistencies or inaccuracies. Validate the information in the dictionary against the actual data sources to ensure integrity. Regular audits help maintain the quality and reliability of the data dictionary, enhancing its value as a reference tool for data analysis and decision-making.
By following these best practices, you can ensure the ongoing usability and integrity of your data dictionary. A well-maintained data dictionary provides a comprehensive and reliable reference for understanding the structure and meaning of your organization’s data, enabling better decision-making and data-driven insights.
Conclusion
Creating a data dictionary is an essential step in any data management process. It not only helps to bring consistency and clarity to your data, but it also improves data governance and enhances collaboration among teams. By documenting the structure, meaning, and relationships of your data elements, you can ensure that everyone involved in your data project is on the same page.
A well-designed data dictionary provides a valuable resource for data analysts, database administrators, and other stakeholders involved in data-related activities. It helps them understand the data they are working with, make informed decisions, and avoid potential data-related issues.
Remember, a well-organized and comprehensive data dictionary can significantly improve the efficiency and accuracy of your data management efforts. So, take the time to create and maintain your data dictionary, and enjoy the benefits of having a clear and easily accessible documentation of your data assets.
FAQs
1. What is a data dictionary?
A data dictionary is a centralized repository that provides detailed information about the data elements used within a database or system. It serves as a reference guide, documenting the structure, definitions, and relationships of the data.
2. Why is a data dictionary important?
A data dictionary is crucial for both technical and non-technical stakeholders. It helps maintain consistency and accuracy of data by providing a common understanding of data elements. It aids in data governance, facilitates data analysis, enhances data quality, and enables effective communication among team members.
3. How to create a data dictionary?
To create a data dictionary, follow these steps:
- Identify the scope and purpose of the data dictionary.
- Document the data elements, including their names, descriptions, and data types.
- Define relationships between the data elements, such as primary keys and foreign keys.
- Include any business rules or constraints associated with the data.
- Regularly update and maintain the data dictionary as changes occur in the system.
4. What should be included in a data dictionary?
A comprehensive data dictionary typically includes the following information:
- Data element names
- Data element descriptions
- Data types and lengths
- Allowed values or ranges
- Source of the data
- Dependencies and relationships
- Data ownership and stewardship
- Data usage and business rules
5. Is a data dictionary only used for databases?
No, a data dictionary can be used for any system or process that involves data. While it is commonly associated with databases, a data dictionary can also be applied to other areas such as data warehouses, data integration systems, business intelligence platforms, and even software applications that require consistent data definitions and documentation.
